Cardiovascular activity of rasagiline, a selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B: comparison with selegiline
- PMID: 15339864
- PMCID: PMC1575354
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705962
Cardiovascular activity of rasagiline, a selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B: comparison with selegiline
Abstract
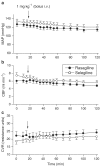
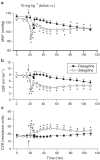
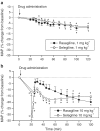
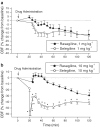
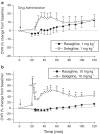
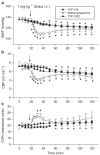
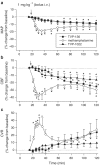
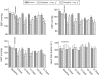
Selegiline is used for treating Parkinson's disease. Despite its efficacy, the clinical use of selegiline in combination with l-dihydroxphenylalanine in Parkinsonian patients is hampered by cardiovascular complications, such as hypotension. This study was designed to compare in rats the cardiovascular effects of selegiline and rasagiline, their metabolites l-methamphetamine and aminoindan (TVP-136), respectively, and the second rasagiline metabolite non-monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor TVP-1022 (N-propargyl-1S(-)aminoindan). Intravenous (i.v.) administration of selegiline and rasagiline (1 mg kg(-1)) to anaesthetized rats (thiobutabarbital, 100 mg kg(-1), i.p.) did not affect mean arterial pressure (MAP), carotid blood flow (CBF) or carotid vascular resistance (CVR). Selegiline (10 mg kg(-1), i.v.) decreased MAP, CBF and increased CVR. In contrast, rasagiline (10 mg kg(-1), i.v.) caused a small transient decrease in MAP, while CBF and CVR were unchanged. l-methamphetamine (1 mg kg(-1), i.v.) administration provoked a dramatic and long-lasting depressor response, decreased CBF and increased CVR. In contrast, injection of aminoindan or TVP-1022 at a similar dose produced gradual nonsignificant decreases in MAP and CBF. Chronic oral treatment (21 days) of awake rats with selegiline at 10 mg kg(-1) decreased systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and MAP, whereas heart rate was unaffected. Since the effective MAO-B inhibitory and clinical dose of rasagiline is about one-tenth that of selegiline, administration of 1 mg kg(-1) day(-1) rasagiline resulted in moderate decreases in SBP, DBP, and MAP, which were significantly lower than those caused by the 10 mg kg(-1) day(-1) dose of selegiline. These findings indicate that rasagiline, when given at doses equivalent to selegiline, is less likely to be hypotensive.
Figures
References
-
- ABU-RAYA S., TABAKMAN R., BLAUGRUND E., TREMBOVLER V., LAZAROVICI P. Neuroprotective and neurotoxic effects of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors and derived metabolites under ischemia in PC12 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002;434:109–116. - PubMed
-
- AM O.B., AMIT T., YOUDIM M.B.H. Contrasting neuroprotective and neurotoxic actions of respective metabolites of anti-Parkinson drugs rasagiline and selegiline. Neurosci. Lett. 2004;355:169–172. - PubMed
-
- ANDREUCCI V.E.Anesthesia for Micropuncture in rats From Manual of Renal Micropuncture 1978Idelson Naoles: Naples, Italy; 43ed. Vittorio E. Andreucci, p
-
- BIRKMAYER W., RIEDERER P., AMBROZI L., YOUDIM M.B.H. Implications of combined treatment with madopar and L-deprenyl in Parkinson disease. Lancet. 1977;2:439–443. - PubMed
-
- BIRKMAYER W., RIEDERER P., YOUDIM M.B.H., LINAUER W. The potentiation of anti-akinetic effect after L-DOPA treatment by an inhibitor of MAO-B deprenyl. J. Neural. Transm. 1975;36:303–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

