MsbA transporter-dependent lipid A 1-dephosphorylation on the periplasmic surface of the inner membrane: topography of francisella novicida LpxE expressed in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15339914
- PMCID: PMC2552400
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M409078200
MsbA transporter-dependent lipid A 1-dephosphorylation on the periplasmic surface of the inner membrane: topography of francisella novicida LpxE expressed in Escherichia coli
Abstract
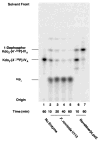
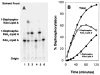
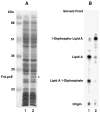
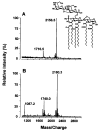
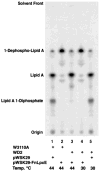
The lipid A anchor of Francisella tularensis lipopolysaccharide (LPS) lacks both phosphate groups present in Escherichia coli lipid A. Membranes of Francisella novicida (an environmental strain related to F. tularensis) contain enzymes that dephosphorylate lipid A and its precursors at the 1- and 4'-positions. We now report the cloning and characterization of a membrane-bound phosphatase of F. novicida that selectively dephosphorylates the 1-position. By transferring an F. novicida genomic DNA library into E. coli and selecting for low level polymyxin resistance, we isolated FnlpxE as the structural gene for the 1-phosphatase, an inner membrane enzyme of 239 amino acid residues. Expression of FnlpxE in a heptose-deficient mutant of E. coli caused massive accumulation of a previously uncharacterized LPS molecule, identified by mass spectrometry as 1-dephospho-Kdo2-lipid A. The predicted periplasmic orientation of the FnLpxE active site suggested that LPS export might be required for 1-dephosphorylation of lipid A. LPS and phospholipid export depend on the activity of MsbA, an essential inner membrane ABC transporter. Expression of FnlpxE in the msbA temperature-sensitive E. coli mutant WD2 resulted in 90% 1-dephosphorylation of lipid A at the permissive temperature (30 degrees C). However, the 1-phosphate group of newly synthesized lipid A was not cleaved at the nonpermissive temperature (44 degrees C). Our findings provide the first direct evidence that lipid A 1-dephosphorylation catalyzed by LpxE occurs on the periplasmic surface of the inner membrane.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression cloning and periplasmic orientation of the Francisella novicida lipid A 4'-phosphatase LpxF.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 7;281(14):9321-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600435200. Epub 2006 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16467300 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli mutants that synthesize dephosphorylated lipid A molecules.Biochemistry. 2010 Sep 28;49(38):8325-37. doi: 10.1021/bi101253s. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20795687 Free PMC article.
-
The Lipid A 1-Phosphatase, LpxE, Functionally Connects Multiple Layers of Bacterial Envelope Biogenesis.mBio. 2019 Jun 18;10(3):e00886-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00886-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31213552 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:295-329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.010307.145803. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17362200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry advances in lipidomica: collision-induced decomposition of Kdo2-lipid A.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005 Sep;77(1-4):131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2004.09.004. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005. PMID: 16099398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Programming Bordetella pertussis lipid A to promote adjuvanticity.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Sep 14;23(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02518-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39272136 Free PMC article.
-
A novel 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) hydrolase that removes the outer Kdo sugar of Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide.J Bacteriol. 2005 May;187(10):3374-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3374-3383.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15866922 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid A Remodeling Is a Pathoadaptive Mechanism That Impacts Lipopolysaccharide Recognition and Intracellular Survival of Burkholderia pseudomallei.Infect Immun. 2018 Sep 21;86(10):e00360-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00360-18. Print 2018 Oct. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30037795 Free PMC article.
-
Periplasmic orientation of nascent lipid A in the inner membrane of an Escherichia coli LptA mutant.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 16;105(37):13823-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807028105. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18768814 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insights into the Lipid A Transport Pathway in MsbA.Structure. 2019 Jul 2;27(7):1114-1123.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 May 23. Structure. 2019. PMID: 31130486 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

