Mutational analysis of arginine 276 in the leucine-loop of human uracil-DNA glycosylase
- PMID: 15339922
- PMCID: PMC3040516
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M407836200
Mutational analysis of arginine 276 in the leucine-loop of human uracil-DNA glycosylase
Abstract
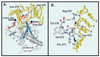
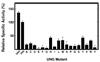
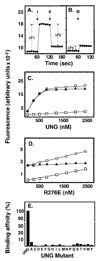
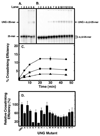
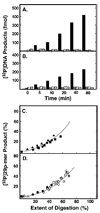
Uracil residues are eliminated from cellular DNA by uracil-DNA glycosylase, which cleaves the N-glycosylic bond between the uracil base and deoxyribose to initiate the uracil-DNA base excision repair pathway. Co-crystal structures of the core catalytic domain of human uracil-DNA glycosylase in complex with uracil-containing DNA suggested that arginine 276 in the highly conserved leucine intercalation loop may be important to enzyme interactions with DNA. To investigate further the role of Arg(276) in enzyme-DNA interactions, PCR-based codon-specific random mutagenesis, and site-specific mutagenesis were performed to construct a library of 18 amino acid changes at Arg(276). All of the R276X mutant proteins formed a stable complex with the uracil-DNA glycosylase inhibitor protein in vitro, indicating that the active site structure of the mutant enzymes was not perturbed. The catalytic activity of the R276X preparations was reduced; the least active mutant, R276E, exhibited 0.6% of wildtype activity, whereas the most active mutant, R276H, exhibited 43%. Equilibrium binding studies utilizing a 2-aminopurine deoxypseudouridine DNA substrate showed that all R276X mutants displayed greatly reduced base flipping/DNA binding. However, the efficiency of UV-catalyzed cross-linking of the R276X mutants to single-stranded DNA was much less compromised. Using a concatemeric [(32)P]U.A DNA polynucleotide substrate to assess enzyme processivity, human uracil-DNA glycosylase was shown to use a processive search mechanism to locate successive uracil residues, and Arg(276) mutations did not alter this attribute.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

