Inactivation of Stat5 in mouse mammary epithelium during pregnancy reveals distinct functions in cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation
- PMID: 15340066
- PMCID: PMC515028
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8037-8047.2004
Inactivation of Stat5 in mouse mammary epithelium during pregnancy reveals distinct functions in cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation
Abstract
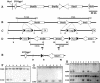
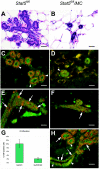
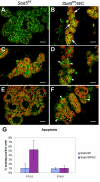
This study explored the functions of the signal transducers and activators of transcription 5a and 5b (referred to as Stat5 here) during different stages of mouse mammary gland development by using conditional gene inactivation. Mammary gland morphogenesis includes cell specification, proliferation and differentiation during pregnancy, cell survival and maintenance of differentiation throughout lactation, and cell death during involution. Stat5 is activated by prolactin, and its presence is mandatory for the proliferation and differentiation of mammary epithelium during pregnancy. To address the question of whether Stat5 is also necessary for the maintenance and survival of the differentiated epithelium, the two genes were deleted at different time points. The 110-kb Stat5 locus in the mouse was bracketed with loxP sites, and its deletion was accomplished by using two Cre-expressing transgenic lines. Loss of Stat5 prior to pregnancy prevented epithelial proliferation and differentiation. Deletion of Stat5 during pregnancy, after mammary epithelium had entered Stat5-mediated differentiation, resulted in premature cell death, indicating that at this stage epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival require Stat5.
Figures



References
-
- Acosta, J. J., R. M. Munoz, L. Gonzalez, A. Subtil-Rodriguez, M. A. Dominguez-Caceres, J. M. Garcia-Martinez, A. Calcabrini, I. Lazaro-Trueba, and J. Martin-Perez. 2003. Src mediates prolactin-dependent proliferation of T47D and MCF7 cells via the activation of focal adhesion kinase/Erk1/2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. Mol. Endocrinol. 17:2268-2282. - PubMed
-
- Bunting, K. D., H. L. Bradley, T. S. Hawley, R. Moriggl, B. P. Sorrentino, and J. N. Ihle. 2002. Reduced lymphomyeloid repopulating activity from adult bone marrow and fetal liver of mice lacking expression of STAT5. Blood 99:479-487. - PubMed
-
- Burdon, T., L. Sankaran, R. J. Wall, M. Spencer, and L. Hennighausen. 1991. Expression of a whey acidic protein transgene during mammary development. Evidence for different mechanisms of regulation during pregnancy and lactation. J. Biol. Chem. 266:6909-6914. - PubMed
-
- Cui, Y., M. Li, K. D. Walton, K. Sun, J. A. Hanover, P. A. Furth, and L. Hennighausen. 2001. The Stat3/5 locus encodes novel endoplasmic reticulum and helicase-like proteins that are preferentially expressed in normal and neoplastic mammary tissue. Genomics 78:129-134. - PubMed
-
- Deng, C., A. Wynshaw-Boris, F. Zhou, A. Kuo, and P. Leder. 1996. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a negative regulator of bone growth. Cell 84:911-921. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
