RELMbeta/FIZZ2 is a goblet cell-specific immune-effector molecule in the gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 15340149
- PMCID: PMC518800
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404034101
RELMbeta/FIZZ2 is a goblet cell-specific immune-effector molecule in the gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
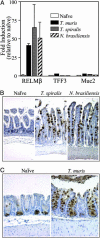
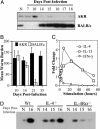
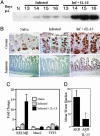
Gastrointestinal (GI) nematode infections are an important public health and economic concern. Experimental studies have shown that resistance to infection requires CD4(+) T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokine responses characterized by the production of IL-4 and IL-13. However, despite >30 years of research, it is unclear how the immune system mediates the expulsion of worms from the GI tract. Here, we demonstrate that a recently described intestinal goblet cell-specific protein, RELMbeta/FIZZ2, is induced after exposure to three phylogenetically distinct GI nematode pathogens. Maximal expression of RELMbeta was coincident with the production of Th2 cytokines and host protective immunity, whereas production of the Th1 cytokine, IFN-gamma, inhibited RELMbeta expression and led to chronic infection. Furthermore, whereas induction of RELMbeta was equivalent in nematode-infected wild-type and IL-4-deficient mice, IL-4 receptor-deficient mice showed minimal RELMbeta induction and developed persistent infections, demonstrating a direct role for IL-13 in optimal expression of RELMbeta. Finally, we show that RELMbeta binds to components of the nematode chemosensory apparatus and inhibits chemotaxic function of a parasitic nematode in vitro. Together, these results suggest that intestinal goblet cell-derived RELMbeta may be a novel Th2 cytokine-induced immune-effector molecule in resistance to GI nematode infection.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. (2001) 54th World Health Assembly: Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections (item 13.3, World Health Organization, Geneva).
-
- Claerebout, E. & Vercruysse, J. (2000) Parasitology 120 S25–S42. - PubMed
-
- Newton, S. E. & Meeusen, E. N. (2003) Parasite Immunol. (Oxf.) 25, 283–296. - PubMed
-
- Maizels, R. M., Bundy, D. A., Selkirk, M. E., Smith, D. F. & Anderson, R. M. (1993) Nature 365, 797–805. - PubMed
-
- Miller, H. R. (1996) Int. J. Parasitol. 26, 801–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI022662/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK 50306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI035914/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 35914/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007066/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI 39368/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI039368/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 07066/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 49780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035914/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- AI22662/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

