Crystallographic identification of Ca2+ and Sr2+ coordination sites in synaptotagmin I C2B domain
- PMID: 15340165
- PMCID: PMC2286539
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.04832604
Crystallographic identification of Ca2+ and Sr2+ coordination sites in synaptotagmin I C2B domain
Abstract
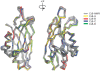
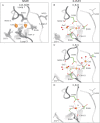
Synaptotagmin I has two tandem Ca(2+)-binding C(2) domains, which are essential for fast synchronous synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. We have solved four crystal structures of the C(2)B domain, one of them in the cation-free form at 1.50 A resolution, two in the Ca(2+)-bound form at 1.04 A (two bound Ca(2+) ions) and 1.65 A (three bound Ca(2+) ions) resolution and one in the Sr(2+)-bound form at 1.18 A (one bound Sr(2+) ion) resolution. The side chains of four highly conserved aspartic acids (D303, D309, D363, and D365) and two main chain oxygens (M302:O and Y364:O), together with water molecules, are in direct contact with two bound Ca(2+) ions (sites 1 and 2). At higher Ca(2+) concentrations, the side chain of N333 rotates and cooperates with D309 to generate a third Ca(2+) coordination site (site 3). Divalent cation binding sites 1 and 2 in the C(2)B domain were previously identified from NMR NOE patterns and titration studies, supplemented by site-directed mutation analysis. One difference between the crystal and NMR studies involves D371, which is not involved in coordination with any of the identified Ca(2+) sites in the crystal structures, while it is coordinated to Ca(2+) in site 2 in the NMR structure. In the presence of Sr(2+), which is also capable of triggering exocytosis, but with lower efficiency, only one cation binding site (site 1) was occupied in the crystallographic structure.
Figures


References
-
- Brunger, A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macro-molecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54 (Pt 5): 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, No. 4. 1994. The CCP4 suite: Programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 50 760–763. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez, I., Arac, D., Ubach, J., Gerber, S.H., Shin, O., Gao, Y., Anderson, R.G., Sudhof, T.C., and Rizo, J. 2001. Three-dimensional structure of the synaptotagmin 1 C2B-domain: Synaptotagmin 1 as a phospholipid binding machine. Neuron 32 1057–1069. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Chacon, R., Konigstorfer, A., Gerber, S.H., Garcia, J., Matos, M.F., Stevens, C.F., Brose, N., Rizo, J., Rosenmund, C., and Sudhof, T.C. 2001. Synaptotagmin I functions as a calcium regulator of release probability. Nature 410 41–49. - PubMed
-
- Geppert, M., Goda, Y., Hammer, R.E., Li, C., Rosahl, T.W., Stevens, C.F., and Sudhof, T.C. 1994. Synaptotagmin I: A major Ca2+ sensor for transmitter release at a central synapse. Cell 79 717–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

