Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: a perspective on the recent advances and the experience with gefitinib
- PMID: 15340373
- PMCID: PMC2750809
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602062
Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: a perspective on the recent advances and the experience with gefitinib
Abstract
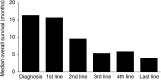
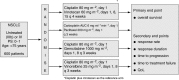
Worldwide, non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality and, until screening detects early disease, treatment for the majority of patients will consist of radiation therapy, chemotherapy or combinations thereof. Modern mono and doublet chemotherapy regimens have translated into modest increases in life expectancy and improved quality of life, but at the expense of systemic and pulmonary adverse events (AEs). There is a great unmet need to provide effective therapy for advanced NSCLC that does not have the toxicity burden of conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Novel drugs that inhibit a range of growth factor receptors, such as the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors gefitinib ('Iressa') and erlotinib ('Tarceva') or the monoclonal antibody cetuximab ('Erbitux'), have recently been evaluated. Having demonstrated antitumour activity and rapid symptom improvement in pretreated patients with advanced NSCLC, gefitinib was approved in the USA, Japan and other countries. Gefitinib is well tolerated with a low incidence of grade 3/4 AEs. Interstitial lung disease has been reported in a small number of patients receiving gefitinib, although this may be attributed to other treatments and conditions. Nevertheless, although the use of novel treatments requires vigilance for unexpected AEs such as pulmonary toxicity, in this area of high unmet clinical need, the benefits outweigh the risks in patients for whom no other proven effective treatment exists.
Figures

References
-
- Bonomi PD, Finkelstein DM, Ruckdeschel JC, Blum RH, Green MD, Mason B, Hahn R, Tormey DC, Harris J, Comis R, Glick J (1989) Combination chemotherapy vs single agents followed by combination chemotherapy in stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer: a study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 7: 1602–1613 - PubMed
-
- Brabender J, Danenberg KD, Metzger R, Schneider PM, Park J, Salonga D, Holscher AH, Danenberg PV (2001) Epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2-neu mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer is correlated with survival. Clin Cancer Res 7: 1850–1855 - PubMed
-
- Crook A, Duffy A, Girling DJ, Souhami RL, Parmar MK (1997) Survey on the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in England and Wales. Eur Respir J 10: 1552–1558 - PubMed
-
- Earle CC, Venditti LN, Neumann PJ, Gelber RD, Weinstein MC, Potosky AL, Weeks JC (2000) Who gets chemotherapy for metastatic lung cancer? Chest 117: 1239–1246 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

