Diagnosis and management of drug-associated interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 15340375
- PMCID: PMC2750814
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602064
Diagnosis and management of drug-associated interstitial lung disease
Abstract
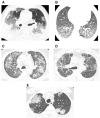
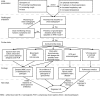
Symptoms of drug-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD) are nonspecific and can be difficult to distinguish from a number of illnesses that commonly occur in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) on therapy. Identification of drug involvement and differentiation from other illnesses is problematic, although radiological manifestations and clinical tests enable many of the alternative causes of symptoms in advanced NSCLC to be excluded. In lung cancer patients, high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is more sensitive than a chest radiograph in evaluating the severity and progression of parenchymal lung disease. Indeed, the use of HRCT imaging has led to the recognition of many distinct patterns of lung involvement and, along with clinical signs and symptoms, helps to predict both outcome and response to treatment. This manuscript outlines the radiology of drug-associated ILD and its differential diagnosis in NSCLC. An algorithm that uses clinical tests to exclude alternative diagnoses is also described.
Figures
References
-
- Abid SH, Malhotra V, Perry MC (2001) Radiation-induced and chemotherapy-induced pulmonary injury. Curr Opin Oncol 13: 242–248 - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society (2002) American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, June 2001 and by The ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165: 277–304 - PubMed
-
- Aviram G, Yu E, Tai P, Lefcoe MS (2001) Computed tomography to assess pulmonary injury associated with concurrent chemo-radiotherapy for inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Can Assoc Radiol J 52: 385–391 - PubMed
-
- Barlesi F, Villani P, Doddoli C, Gimenez C, Kleisbauer JP (2004) Gemcitabine-induced severe pulmonary toxicity. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 18: 85–91 - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Lower EE, Lynch JP (1994) Treatment modalities for sarcoidosis. Clin Pulm Med 1: 223–231
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

