CD1d-restricted T cell activation by nonlipidic small molecules
- PMID: 15342907
- PMCID: PMC518797
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402838101
CD1d-restricted T cell activation by nonlipidic small molecules
Abstract
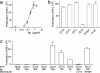
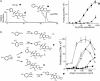
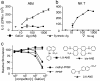
In addition to NK T cells expressing invariant Valpha14 or Valpha24 T cell receptors (TCRs), the CD1d-restricted T cell repertoire is comprised of T cells with diverse TCRs that mediate inflammation during autoimmune and infectious disease. Here we describe the isolation of human Valpha24(-) T cells that are activated by antigen and CD1d. Mass spectrometric and NMR studies revealed that the stimulatory compounds were neither peptidic nor lipidic but instead were composed of sulfur and aromatic hydrocarbon rings, corresponding to the general structure of phenyl pentamethyldihydrobenzofuran sulfonates. Studies of the molecular mechanism of T cell activation showed that a clonotypic Valpha2/Vbeta21 TCR transmitted activating signals, which were highly specific for hydroxylation and methylation patterns at the terminal structures of stimulatory compounds. These studies provide evidence for noninvariant CD1d-restricted T cells in humans and identify the complete molecular structure of a nonlipidic small molecule that activates T cells through an alphabeta TCR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Conserved and heterogeneous lipid antigen specificities of CD1d-restricted NKT cell receptors.J Immunol. 2006 Mar 15;176(6):3625-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.6.3625. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16517731
-
Benzofuran sulfonates and small self-lipid antigens activate type II NKT cells via CD1d.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 24;118(34):e2104420118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2104420118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34417291 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen specificity of semi-invariant CD1d-restricted T cell receptors: the best of both worlds?Immunol Cell Biol. 2004 Jun;82(3):285-94. doi: 10.1111/j.0818-9641.2004.01257.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15186260 Review.
-
The mouse CD1d-restricted repertoire is dominated by a few autoreactive T cell receptor families.J Exp Med. 2001 Apr 16;193(8):893-904. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.8.893. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11304550 Free PMC article.
-
TCR-mediated recognition of glycolipid CD1 complexes.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;314:165-93. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-69511-0_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17593661 Review.
Cited by
-
T cells specific for lipid antigens.Immunol Res. 2012 Sep;53(1-3):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8294-6. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22427014 Review.
-
The processing and presentation of lipids and glycolipids to the immune system.Immunol Rev. 2016 Jul;272(1):109-19. doi: 10.1111/imr.12431. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27319346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid and small-molecule display by CD1 and MR1.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Oct;15(10):643-54. doi: 10.1038/nri3889. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26388332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exacerbated susceptibility to infection-stimulated immunopathology in CD1d-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 15;174(12):7904-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.7904. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15944296 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-associated lysophospholipids as ligands for CD1d-restricted T cells in human cancer.Blood. 2008 Aug 15;112(4):1308-16. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-149831. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18535199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Porcelli, S., Morita, C. T. & Brenner, M. B. (1992) Nature 360, 593–597. - PubMed
-
- Beckman, E. M., Melian, A., Behar, S. M., Sieling, P. A., Chatterjee, D., Furlong, S. T., Matsumoto, R., Rosat, J. P., Modlin, R. L. & Porcelli, S. A. (1996) J. Immunol. 157, 2795–2803. - PubMed
-
- Rosat, J. P., Grant, E. P., Beckman, E. M., Dascher, C. C., Sieling, P. A., Frederique, D., Modlin, R. L., Porcelli, S. A., Furlong, S. T. & Brenner, M. B. (1999) J. Immunol. 162, 366–371. - PubMed
-
- Beckman, E. M., Porcelli, S. A., Morita, C. T., Behar, S. M., Furlong, S. T. & Brenner, M. B. (1994) Nature 372, 691–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

