Anti-C1q autoantibodies deposit in glomeruli but are only pathogenic in combination with glomerular C1q-containing immune complexes
- PMID: 15343386
- PMCID: PMC514584
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI21075
Anti-C1q autoantibodies deposit in glomeruli but are only pathogenic in combination with glomerular C1q-containing immune complexes
Abstract
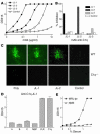
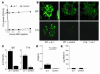
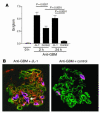
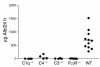
Anti-C1q autoantibodies are present in sera of patients with several autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Strikingly, in SLE the presence of anti-C1q is associated with the occurrence of nephritis. We have generated mouse anti-mouse C1q mAb's and used murine models to investigate whether anti-C1q autoantibodies actually contribute to renal pathology in glomerular immune complex disease. Administration of anti-C1q mAb JL-1, which recognizes the collagen-like region of C1q, resulted in glomerular deposition of C1q and anti-C1q autoantibodies and mild granulocyte influx, but no overt renal damage. However, combination of JL-1 with a subnephritogenic dose of C1q-fixing anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) antibodies enhanced renal damage characterized by persistently increased levels of infiltrating granulocytes, major histological changes, and increased albuminuria. This was not observed when a non-C1q-fixing anti-GBM preparation was used. Experiments with different knockout mice showed that renal damage was dependent not only on glomerular C1q and complement activation but also on Fcgamma receptors. In conclusion, anti-C1q autoantibodies deposit in glomeruli together with C1q but induce overt renal disease only in the context of glomerular immune complex disease. This provides an explanation why anti-C1q antibodies are especially pathogenic in patients with SLE.
Figures





Comment in
-
Anti-C1q autoantibodies amplify pathogenic complement activation in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Invest. 2004 Sep;114(5):616-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI22820. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15343378 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Glomerular deposition of C1q and anti-C1q antibodies in mice following injection of antimouse C1q antibodies.Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Apr;132(1):32-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02108.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12653833 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-C1q autoantibodies amplify pathogenic complement activation in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Invest. 2004 Sep;114(5):616-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI22820. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15343378 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular C1q deposition and serum anti-C1q antibodies in anti-glomerular basement membrane disease.BMC Immunol. 2013 Sep 21;14:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-42. BMC Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24053688 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and pathologic considerations of the qualitative and quantitative aspects of lupus nephritogenic autoantibodies: A comprehensive review.J Autoimmun. 2016 May;69:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 26879422 Review.
-
C1q and systemic lupus erythematosus.Immunobiology. 1998 Aug;199(2):265-85. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(98)80032-6. Immunobiology. 1998. PMID: 9777411 Review.
Cited by
-
Early systemic microvascular damage in pigs with atherogenic diabetes mellitus coincides with renal angiopoietin dysbalance.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0121555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121555. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909188 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus nephritis: an overview of recent findings.Autoimmune Dis. 2012;2012:849684. doi: 10.1155/2012/849684. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Autoimmune Dis. 2012. PMID: 22536486 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular antibodies in lupus nephritis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Jun;40(3):151-8. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8204-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20414746 Review.
-
Are anti-C1q antibodies different from other SLE autoantibodies?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Aug;6(8):490-3. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.56. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20421881 Review.
-
Anti-C1q autoantibodies, novel tests, and clinical consequences.Front Immunol. 2013 May 14;4:117. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00117. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23717311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipsky PE. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:764–766. - PubMed
-
- Mills JA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;330:1871–1879. - PubMed
-
- Tsao BP. The genetics of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:595–602. - PubMed
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. First of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1058–1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

