Molecular characterization of CcpA and involvement of this protein in transcriptional regulation of lactate dehydrogenase and pyruvate formate-lyase in the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis
- PMID: 15345406
- PMCID: PMC520867
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5244-5251.2004
Molecular characterization of CcpA and involvement of this protein in transcriptional regulation of lactate dehydrogenase and pyruvate formate-lyase in the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis
Abstract
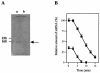
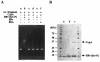
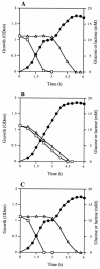
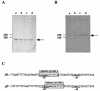
A ccpA gene that encodes global catabolite control protein A (CcpA) in Streptococcus bovis was identified and characterized, and the involvement of CcpA in transcriptional control of a gene (ldh) encoding lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and a gene (pfl) encoding pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) was examined. The ccpA gene was shown to be transcribed as a monocistronic operon. A catabolite-responsive element (cre) was found in the promoter region of ccpA, suggesting that ccpA transcription in S. bovis is autogenously regulated. CcpA required HPr that was phosphorylated at the serine residue at position 46 (HPr-[Ser-P]) for binding to the cre site, but glucose 6-phosphate, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, and NADP had no effect on binding. Diauxic growth was observed when S. bovis was grown in a medium containing glucose and lactose, but it disappeared when ccpA was disrupted, which indicates that CcpA is involved in catabolite repression in S. bovis. The level of ccpA mRNA was higher when cells were grown on glucose than when they were grown on lactose, which was in line with the level of ldh mRNA. When cells were grown on glucose, the ldh mRNA level was lower but the pfl mRNA level was higher in a ccpA-disrupted mutant than in the parent strain, which suggests that ldh transcription is enhanced and pfl transcription is suppressed by CcpA. The ccpA-disrupted mutant produced less lactate and more formate than the parent, probably because the mutant had reduced LDH activity and elevated PFL activity. In the upper region of both ldh and pfl, a cre-like sequence was found, suggesting that the complex consisting of CcpA and HPr-[Ser-P] binds to the possible cre sites. Thus, CcpA appears to be involved in the global regulation of sugar utilization in S. bovis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding pyruvate formate-lyase of a ruminal bacterium, Streptococcus bovis.Microbiology (Reading). 1999 Jan;145 ( Pt 1):151-157. doi: 10.1099/13500872-145-1-151. Microbiology (Reading). 1999. PMID: 10206694
-
Effects of the overexpression of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase on fermentation pattern and transcription of the genes encoding lactate dehydrogenase and pyruvate formate-lyase in a ruminal bacterium, Streptococcus bovis.J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2004 Apr;50(2):71-8. doi: 10.2323/jgam.50.71. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15248145
-
Presence of NAD+-specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and CcpA-dependent transcription of its gene in the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Apr;257(1):17-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00111.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16553827
-
Carbon catabolite repression by the catabolite control protein CcpA in Staphylococcus xylosus.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 May;4(3):309-14. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11931563 Review.
-
Catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: a global regulatory mechanism for the gram-positive bacteria?Mol Microbiol. 1995 Feb;15(3):395-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02252.x. Mol Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7540244 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Glucose and Starch on Lactate Production by Newly Isolated Streptococcus bovis S1 from Saanen Goats.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Sep 16;82(19):5982-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01994-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27474714 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional control of carbohydrate catabolism by the CcpA protein in the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;89(10):e0047423. doi: 10.1128/aem.00474-23. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37823652 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and Overexpression of the als, pflA, and adhB Genes in Streptococcus thermophilus and Their Effects on Metabolite Formation.Mol Biotechnol. 2015 Oct;57(10):923-30. doi: 10.1007/s12033-015-9882-1. Mol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26280324
-
How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Dec;70(4):939-1031. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 17158705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties and role of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in the control of fermentation pattern and growth in a ruminal bacterium, Streptococcus bovis.Curr Microbiol. 2009 Apr;58(4):283-7. doi: 10.1007/s00284-008-9326-2. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Curr Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19034572
References
-
- Asanuma, N., and T. Hino. 1997. Tolerance to low pH and lactate production in rumen bacteria. Anim. Sci. Technol. 68:367-376.
-
- Asanuma, N., and T. Hino. 2002. Fructose bisphosphate aldolase activity and glycolytic intermediate concentrations in relation to lactate production in Streptococcus bovis. Anaerobe 8:1-8.
-
- Asanuma, N., and T. Hino. 2003. Molecular characterization of HPr and related enzymes, and regulation of HPr phosphorylation in the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis. Arch. Microbiol. 179:205-213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

