Interleukin 10 promoter microsatellite polymorphisms are associated with response to long term treatment with etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15345504
- PMCID: PMC1755447
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.027672
Interleukin 10 promoter microsatellite polymorphisms are associated with response to long term treatment with etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse the association of interleukin 10 (IL10) promoter polymorphisms, which have been shown to be related to IL10 secretion capacity, with the response to long term treatment with etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Fifty patients with active RA were treated for up to 4 years (median 39 months, range 3-52) with stable doses of etanercept as monotherapy. Treatment response was assessed as defined by the EULAR criteria in an intention to treat analysis, with the last observation carried forward. IL10 promoter microsatellite polymorphisms IL10.R and IL10.G were genotyped by fragment length analysis in patients and 189 healthy controls matched for ethnicity, age, and sex. Haplotypes were reconstructed using a method based on bayesian, coalescent theory with the PHASE software.
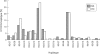
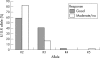
Results: IL10 microsatellite polymorphisms were not associated with susceptibility to RA. When patients with good treatment response (n = 25) were compared with patients with moderate (n = 17) or no response (n = 8), a significantly different distribution of the prevailing alleles R2, R3 and G9, G13, respectively, became evident. Good treatment response was associated with carriage of the R3 allele or R3-G9 haplotype, whereas the allele G13 and the haplotype R2-G13 predominated in patients with moderate or no response.
Conclusion: Genotyping of the IL10 promoter microsatellites may be useful in predicting the clinical response to etanercept in patients with RA. The high prevalence of the presumptive IL10 low producer allele R3 in patients with a favourable response suggests that IL10 promotes disease activity in RA under the specific condition of tumour necrosis factor antagonism.
Figures

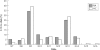
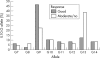
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

