Lipoprotein(a): an elusive cardiovascular risk factor
- PMID: 15345512
- PMCID: PMC3275911
- DOI: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000144010.55563.63
Lipoprotein(a): an elusive cardiovascular risk factor
Abstract
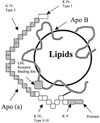
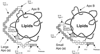
Lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)], is present only in humans, Old World nonhuman primates, and the European hedgehog. Lp(a) has many properties in common with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) but contains a unique protein, apo(a), which is structurally different from other apolipoproteins. The size of the apo(a) gene is highly variable, resulting in the protein molecular weight ranging from 300 to 800 kDa; this large variation may be caused by neutral evolution in the absence of any selection advantage. Apo(a) influences to a major extent metabolic and physicochemical properties of Lp(a), and the size polymorphism of the apo(a) gene contributes to the pronounced heterogeneity of Lp(a). There is an inverse relationship between apo(a) size and Lp(a) levels; however, this pattern is complex. For a given apo(a) size, there is a considerable variation in Lp(a) levels across individuals, underscoring the importance to assess allele-specific Lp(a) levels. Further, Lp(a) levels differ between populations, and blacks have generally higher levels than Asians and whites, adjusting for apo(a) sizes. In addition to the apo(a) size polymorphism, an upstream pentanucleotide repeat (TTTTA(n)) affects Lp(a) levels. Several meta-analyses have provided support for an association between Lp(a) and coronary artery disease, and the levels of Lp(a) carried in particles with smaller size apo(a) isoforms are associated with cardiovascular disease or with preclinical vascular changes. Further, there is an interaction between Lp(a) and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The physiological role of Lp(a) is unknown, although a majority of studies implicate Lp(a) as a risk factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LPA gene: interaction between the apolipoprotein(a) size ('kringle IV' repeat) polymorphism and a pentanucleotide repeat polymorphism influences Lp(a) lipoprotein level.J Intern Med. 2000 Jan;247(1):139-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2000.00628.x. J Intern Med. 2000. PMID: 10672142
-
Enigmatic role of lipoprotein(a) in cardiovascular disease.Clin Transl Sci. 2010 Dec;3(6):327-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2010.00238.x. Clin Transl Sci. 2010. PMID: 21167011 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of apolipoprotein(a) size, pentanucleotide TTTTA repeat and C/T(+93) polymorphisms of the apo(a) gene to regulation of lipoprotein(a) plasma levels in a population of young European Caucasians.Atherosclerosis. 1999 Nov 1;147(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(99)00137-9. Atherosclerosis. 1999. PMID: 10525120
-
Novel insights into Lp(a) physiology and pathogenicity: more questions than answers?Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Dec;6(4):267-78. doi: 10.2174/187152906779010764. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 17378772 Review.
-
Lipoprotein(a), atherosclerosis, and apolipoprotein(a) gene polymorphism.Mol Genet Metab. 2000 Sep-Oct;71(1-2):87-92. doi: 10.1006/mgme.2000.3070. Mol Genet Metab. 2000. PMID: 11001801 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlations Between Coronary Artery Disease, Coronary Artery Calcium Score, and Lipoprotein(a) Level in Korea.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Oct 1;18:981-987. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S374372. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 36212048 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized phospholipids and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as important determinants of Lp(a) functionality and pathophysiological role.J Biomed Res. 2018 Jan 26;31(1):13-22. doi: 10.7555/JBR.31.20160009. J Biomed Res. 2018. PMID: 27346583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoprotein(a) and atherosclerosis: new perspectives on the mechanism of action of an enigmatic lipoprotein.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2005 Sep;7(5):389-95. doi: 10.1007/s11883-005-0052-y. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2005. PMID: 16105483 Review.
-
Haplotype of the Lipoprotein(a) Gene Variants rs10455872 and rs3798220 Is Associated with Parameters of Coagulation, Fibrinolysis, and Inflammation in Patients after Myocardial Infarction and Highly Elevated Lipoprotein(a) Values.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 6;25(2):736. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020736. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255810 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular risk factors in portuguese obese children and adolescents: impact of small reductions in body mass index imposed by lifestyle modifications.Open Biochem J. 2012;6:43-50. doi: 10.2174/1874091X01206010043. Epub 2012 May 11. Open Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22629286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg K. A new serum system in man: the Lp system. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:362–382. - PubMed
-
- Albers JJ, Cabana VG, Warnick GR, Hazzard WR. Lp(a) lipoprotein: relationship to sinking pre-β lipoprotein, hyperlipoproteinemia, and apolipoprotein B. Metabolism. 1975;24:1047–1054. - PubMed
-
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a) Science (Washington DC) 1989;246:904–910. - PubMed
-
- Marcovina SM, Koschinsky ML. Lipoprotein (a): Structure, measurement, and clinical significance. In: Rifai N, Warnick GR, Dominiczak MH, editors. Handbook of Lipoprotein Testing. Washington, DC: AACC Press; 1997. pp. 283–313.
-
- Gaubatz JW, Heideman C, Gotto AM, Jr, Morrisett JD, Dahlén GH. Human plasma lipoprotein(a): structural properties. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:4582–4589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

