Wide nanoscopic pore of maxi-anion channel suits its function as an ATP-conductive pathway
- PMID: 15345546
- PMCID: PMC1304572
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.043174
Wide nanoscopic pore of maxi-anion channel suits its function as an ATP-conductive pathway
Abstract
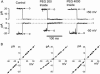
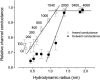
The newly proposed function of the maxi-anion channel as a conductive pathway for ATP release requires that its pore is sufficiently large to permit passage of a bulky ATP(4-) anion. We found a linear relationship between relative permeability of organic anions of different size and their relative ionic mobility (measured as the ratio of ionic conductance) with a slope close to 1, suggesting that organic anions tested with radii up to 0.49 nm (lactobionate) move inside the channel by free diffusion. In the second approach, we, for the first time, succeeded in pore sizing by the nonelectrolyte exclusion method in single-channel patch-clamp experiments. The cutoff radii of PEG molecules that could access the channel from intracellular (1.16 nm) and extracellular (1.42 nm) sides indicated an asymmetry of the two entrances to the channel pore. Measurements by symmetrical two-sided application of PEG molecules yielded an average functional pore radius of approximately 1.3 nm. These three estimates are considerably larger than the radius of ATP(4-) (0.57-0.65 nm) and MgATP(2-) (approximately 0.60 nm). We therefore conclude that the nanoscopic maxi-anion channel pore provides sufficient room to accommodate ATP and is well suited to its function as a conductive pathway for ATP release in cell-to-cell communication.
Figures

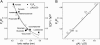



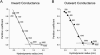
Similar articles
-
Sizing the pore of the volume-sensitive anion channel by differential polymer partitioning.FEBS Lett. 2004 Oct 22;576(3):433-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.051. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15498575
-
Molecular Identities and ATP Release Activities of Two Types of Volume-Regulatory Anion Channels, VSOR and Maxi-Cl.Curr Top Membr. 2018;81:125-176. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Curr Top Membr. 2018. PMID: 30243431 Review.
-
Plasmalemmal VDAC controversies and maxi-anion channel puzzle.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1818(6):1570-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.09.024. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21986486 Review.
-
Polymeric nonelectrolytes to probe pore geometry: application to the alpha-toxin transmembrane channel.Biophys J. 1999 Dec;77(6):3023-33. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77133-X. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10585924 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ATP-conductive anion channel in ATP release from neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in ischaemic or hypoxic conditions.J Physiol. 2004 Sep 15;559(Pt 3):799-812. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.069245. Epub 2004 Jul 22. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15272030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Swelling-activated anion channels are essential for volume regulation of mouse thymocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):9125-37. doi: 10.3390/ijms12129125. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22272123 Free PMC article.
-
The ATP-Releasing Maxi-Cl Channel: Its Identity, Molecular Partners and Physiological/Pathophysiological Implications.Life (Basel). 2021 May 31;11(6):509. doi: 10.3390/life11060509. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanometer-Scale Permeabilization and Osmotic Swelling Induced by 5-ns Pulsed Electric Fields.J Membr Biol. 2017 Feb;250(1):21-30. doi: 10.1007/s00232-016-9918-x. Epub 2016 Jul 19. J Membr Biol. 2017. PMID: 27435216
-
Mechanisms of Pannexin 1 (PANX1) Channel Mechanosensitivity and Its Pathological Roles.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1523. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031523. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological comparison of swelling-activated excitatory amino acid release and Cl- currents in cultured rat astrocytes.J Physiol. 2006 May 1;572(Pt 3):677-89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.103820. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16527858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahamonde, M. I., J. M. Fernandez-Fernandez, F. X. Guix, E. Vazquez, and M. A. Valverde. 2003. Plasma membrane voltage-dependent anion channel mediates anti-estrogen-activated maxi Cl− currents in C1300 neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278:33284–33289. - PubMed
-
- Bahamonde, M. I., and M. A. Valverde. 2003. Voltage-dependent anion channel localises to the plasma membrane and peripheral but not perinuclear mitochondria. Pflugers Arch. 446:309–313. - PubMed
-
- Bathori, G., I. Parolini, F. Tombola, I. Szabo, A. Messina, M. Oliva, V. De Pinto, M. Lisanti, M. Sargiacomo, and M. Zoratti. 1999. Porin is present in the plasma membrane where it is concentrated in caveolae and caveolae-related domains. J. Biol. Chem. 274:29607–29612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

