A Brownian dynamics study of the interaction of Phormidium laminosum plastocyanin with Phormidium laminosum cytochrome f
- PMID: 15345580
- PMCID: PMC1304607
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.103.038497
A Brownian dynamics study of the interaction of Phormidium laminosum plastocyanin with Phormidium laminosum cytochrome f
Abstract
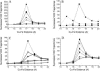
The interaction of Phormidium laminosum plastocyanin (PC) with P. laminosum cytochrome f (cyt f) was studied using Brownian dynamics (BD) simulations. Few complexes and a low rate of electron transfer were observed for wild-type PC. Increasing the positive electrostatic field on PC by the addition of a Zn(2+) ion in the neighborhood of D44 and D45 on PC (as found in crystal structure of plastocyanin) increased the number of complexes formed and the calculated rates of electron transfer as did PC mutations D44A, D45A, E54A, and E57A. Mutations of charged residues on Phormidium PC and Phormidium cyt f were used to map binding sites on both proteins. In both the presence and absence of the Zn(2+) ion, the following residues on PC interact with cyt f: D44, D45, K6, D79, R93, and K100 that lie in a patch just below H92 and Y88 and D10, E17, and E70 located on the upper portion of the PC molecule. In the absence of the Zn(2+) ion, K6 and K35 on the top of the PC molecule also interact with cyt f. Cyt f residues involved in binding PC, in the absence of the Zn(2+) ion, include E165, D187, and D188 that are located on the small domain of cyt f. The orientation of PC in the complexes was quite random in accordance with NMR results. In the presence of the Zn(2+) ion, K53 and E54 in the lower patch of the PC molecule also interact with cyt f and PC interacts with E86, E95, and E123 on the large domain of cyt f. Also, the orientation of PC in the complexes was much more uniform than in the absence of the Zn(2+) ion. The difference may be due to both the larger electrostatic field and the greater asymmetry of the charge distribution on PC observed in the presence of the Zn(2+) ion. Hydrophobic interactions were also observed suggesting a model of cyt f-PC interactions in which electrostatic forces bring the two molecules together but hydrophobic interactions participate in stabilizing the final electron-transfer-active dock.
Figures





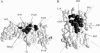
Similar articles
-
A Brownian dynamics study of the interaction of Phormidium cytochrome f with various cyanobacterial plastocyanins.Biophys J. 2006 Jan 1;90(1):366-80. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.065185. Epub 2005 Oct 7. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16214856 Free PMC article.
-
Brownian dynamics study of cytochrome f interactions with cytochrome c6 and plastocyanin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii plastocyanin, and cytochrome c6 mutants.Biophys J. 2005 Mar;88(3):2323-39. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.053561. Epub 2004 Dec 30. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15626695 Free PMC article.
-
Brownian dynamics simulations of the interaction of Chlamydomonas cytochrome f with plastocyanin and cytochrome c6.Biophys J. 2003 Sep;85(3):2055-68. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74633-5. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 12944318 Free PMC article.
-
Weak interactions and molecular recognition in systems involving electron transfer proteins.Chem Rec. 2001;1(4):290-9. doi: 10.1002/tcr.1014. Chem Rec. 2001. PMID: 11893069 Review.
-
The cytochrome f-plastocyanin complex as a model to study transient interactions between redox proteins.FEBS Lett. 2012 Mar 9;586(5):646-52. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.08.035. Epub 2011 Aug 30. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 21889503 Review.
Cited by
-
A Brownian dynamics study of the effects of cytochrome f structure and deletion of its small domain in interactions with cytochrome c6 and plastocyanin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Biophys J. 2006 Jan 15;90(2):566-77. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.067058. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16239335 Free PMC article.
-
A Brownian dynamics study of the interaction of Phormidium cytochrome f with various cyanobacterial plastocyanins.Biophys J. 2006 Jan 1;90(1):366-80. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.065185. Epub 2005 Oct 7. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16214856 Free PMC article.
-
A Brownian Dynamics computational study of the interaction of spinach plastocyanin with turnip cytochrome f: the importance of plastocyanin conformational changes.Photosynth Res. 2007 Nov-Dec;94(2-3):411-22. doi: 10.1007/s11120-007-9192-y. Epub 2007 Oct 31. Photosynth Res. 2007. PMID: 17972160
-
Brownian dynamics study of cytochrome f interactions with cytochrome c6 and plastocyanin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii plastocyanin, and cytochrome c6 mutants.Biophys J. 2005 Mar;88(3):2323-39. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.053561. Epub 2004 Dec 30. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15626695 Free PMC article.
-
Lysozyme dimerization: Brownian dynamics simulation.J Mol Model. 2005 Dec;12(1):34-41. doi: 10.1007/s00894-005-0001-2. Epub 2005 Aug 18. J Mol Model. 2005. PMID: 16133093
References
-
- Anderson, G. P., D. G. Sanderson, C. H. Lee, S. Durell, L. B. Anderson, and E. L. Gross. 1987. The effect of ethylene diamine chemical modification of plastocyanin on the rate of cytochrome f oxidation and P-700+ reduction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 894:386–398. - PubMed
-
- Bond, C. S., D. S. Bendall, H. C. Freeman, J. M. Guss, C. J. Howe, M. J. Wagner, and M. C. Wilce. 1999. The structure of plastocyanin from the cyanobacterium Phormidium laminosum. Acta Crystal. D55:414–421. - PubMed
-
- Carrell, C. J., B. G. Schlarb, D. S. Bendall, C. J. Howe, W. A. Cramer, and J. L. Smith. 1999. Structure of the soluble domain of cytochrome f from the cyanobacterium Phormidium laminosum. Biochemistry. 38:9590–9599. - PubMed
-
- Chi, Y. I., L. S. Huang, Z. Zhang, J. G. Fernandez-Velasco, and E. A. Berry. 2000. X-ray structure of a truncated form of cytochrome f from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochemistry. 39:7689–7701. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

