A mitochondrial oscillator dependent on reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 15345581
- PMCID: PMC1304608
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.041749
A mitochondrial oscillator dependent on reactive oxygen species
Abstract
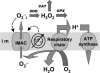
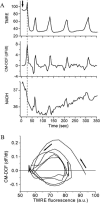
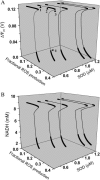
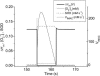
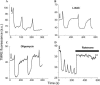
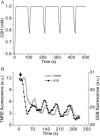
We describe a unique mitochondrial oscillator that depends on oxidative phosphorylation, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and mitochondrial inner membrane ion channels. Cell-wide synchronized oscillations in mitochondrial membrane potential (Delta Psi(m)), NADH, and ROS production have been recently described in isolated cardiomyocytes, and we have hypothesized that the balance between superoxide anion efflux through inner membrane anion channels and the intracellular ROS scavenging capacity play a key role in the oscillatory mechanism. Here, we formally test the hypothesis using a computational model of mitochondrial energetics and Ca(2+) handling including mitochondrial ROS production, cytoplasmic ROS scavenging, and ROS activation of inner membrane anion flux. The mathematical model reproduces the period and phase of the observed oscillations in Delta Psi(m), NADH, and ROS. Moreover, we experimentally verify model predictions that the period of the oscillator can be modulated by altering the concentration of ROS scavengers or the rate of oxidative phosphorylation, and that the redox state of the glutathione pool oscillates. In addition to its role in cellular dysfunction during metabolic stress, the period of the oscillator can be shown to span a wide range, from milliseconds to hours, suggesting that it may also be a mechanism for physiological timekeeping and/or redox signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dynamic modulation of Ca2+ sparks by mitochondrial oscillations in isolated guinea pig cardiomyocytes under oxidative stress.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Nov;51(5):632-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.05.007. Epub 2011 May 27. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21645518 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione oxidation as a trigger of mitochondrial depolarization and oscillation in intact hearts.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008 Nov;45(5):650-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.07.017. Epub 2008 Aug 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18760283 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-optimized ROS balance: a unifying hypothesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jun-Jul;1797(6-7):865-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.02.016. Epub 2010 Feb 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20175987 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial oscillations in physiology and pathophysiology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;641:98-117. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-09794-7_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18783175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: an update and review.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May-Jun;1757(5-6):509-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.04.029. Epub 2006 May 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16829228 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling the detailed kinetics of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase: Catalytic mechanism and nitric oxide inhibition.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016 Nov 1;121(5):1196-1207. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00524.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016. PMID: 27633738 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy in free radical generation is blunted by high-fat diet induced alterations in skeletal muscle mitochondrial metabolism.Biophys J. 2013 Mar 5;104(5):1127-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.01.025. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23473496 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial responses in cultured rat hippocampal neurons exposed to micromolar concentrations of TMRM.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058059. Epub 2013 Mar 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23483968 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac mitochondria and arrhythmias.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Nov 1;88(2):241-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq231. Epub 2010 Jul 9. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20621924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioenergetics of life, disease and death phenomena.Theory Biosci. 2018 Nov;137(2):155-168. doi: 10.1007/s12064-018-0266-5. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Theory Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29992378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aebi, H. 1984. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 105:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Aon, M. A., and S. Cortassa. 1997. Dynamic Biological Organization. Fundamentals as Applied to Cellular Systems. Chapman & Hall, London, UK.
-
- Aon, M. A., S. Cortassa, E. Marban, and B. O'Rourke. 2003. Synchronized whole-cell oscillations in mitochondrial metabolism triggered by a local release of reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 278:44735–44744. - PubMed
-
- Bak, P., C. Tang, and K. Wiesenfeld. 1987. Self-organized criticality: an explanation of the 1/f noise. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59:381–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

