Activation of PI3K is indispensable for interleukin 7-mediated viability, proliferation, glucose use, and growth of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
- PMID: 15353558
- PMCID: PMC2212738
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040789
Activation of PI3K is indispensable for interleukin 7-mediated viability, proliferation, glucose use, and growth of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Abstract
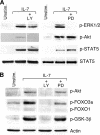
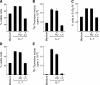
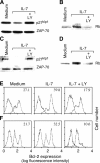
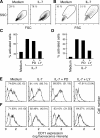
Interleukin (IL)-7 is essential for normal T cell development. Previously, we have shown that IL-7 increases viability and proliferation of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells by up-regulating Bcl-2 and down-regulating the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1. Here, we examined the signaling pathways via which IL-7 mediates these effects. We investigated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt (protein kinase B) pathways, which have active roles in T cell expansion and have been implicated in tumorigenesis. IL-7 induced activation of the MEK-Erk pathway in T-ALL cells; however, inhibition of the MEK-Erk pathway by the use of the cell-permeable inhibitor PD98059, did not affect IL-7-mediated viability or cell cycle progression of leukemic cells. IL-7 induced PI3K-dependent phosphorylation of Akt and its downstream targets GSK-3, FOXO1, and FOXO3a. PI3K activation was mandatory for IL-7-mediated Bcl-2 up-regulation, p27kip1 down-regulation, Rb hyperphosphorylation, and consequent viability and cell cycle progression of T-ALL cells. PI3K signaling was also required for cell size increase, up-regulation of CD71, expression of the glucose transporter Glut1, uptake of glucose, and maintenance of mitochondrial integrity. Our results implicate PI3K as a major effector of IL-7-induced viability, metabolic activation, growth and proliferation of T-ALL cells, and suggest that PI3K and its downstream effectors may represent molecular targets for therapeutic intervention in T-ALL.
Figures

References
-
- von Freeden-Jeffry, U., N. Solvason, M. Howard, and R. Murray. 1997. The earliest T lineage-committed cells depend on IL-7 for Bcl-2 expression and normal cell cycle progression. Immunity. 7:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Dibirdik, I., M.C. Langlie, J.A. Ledbetter, L. Tuel-Ahlgren, V. Obuz, K.G. Waddick, K. Gajl-Peczalska, G.L. Schieven, and F.M. Uckun. 1991. Engagement of interleukin-7 receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation, phosphoinositide turnover, and clonal proliferation of human T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood. 78:564–570. - PubMed
-
- Karawajew, L., V. Ruppert, C. Wuchter, A. Kosser, M. Schrappe, B. Dorken, and W.D. Ludwig. 2000. Inhibition of in vitro spontaneous apoptosis by IL-7 correlates with bcl-2 up-regulation, cortical/mature immunophenotype, and better early cytoreduction of childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 96:297–306. - PubMed
-
- Funk, P.E., R.P. Stephan, and P.L. Witte. 1995. Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1-positive reticular cells express interleukin-7 and stem cell factor in the bone marrow. Blood. 86:2661–2671. - PubMed
-
- Oosterwegel, M.A., M.C. Haks, U. Jeffry, R. Murray, and A.M. Kruisbeek. 1997. Induction of TCR gene rearrangements in uncommitted stem cells by a subset of IL-7 producing, MHC class-II-expressing thymic stromal cells. Immunity. 6:351–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

