NF-kappa B-mediated repression of growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins 45alpha and gamma is essential for cancer cell survival
- PMID: 15353598
- PMCID: PMC518803
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402069101
NF-kappa B-mediated repression of growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins 45alpha and gamma is essential for cancer cell survival
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 19;101(42):15271. Zhou, Jin-Rhong [corrected to Zhou, Jin-Rong]
Abstract
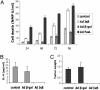
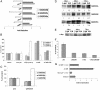
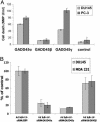
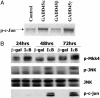
The NF-kappaB/IkappaB signaling pathway is a critical regulator of cell survival in cancer. Here, we report that combined down-regulation of growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins (GADD)45alpha and gamma expression by NF-kappaB is an essential step for various cancer types to escape programmed cell death. We demonstrate that inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells results in GADD45alpha- and gamma-dependent induction of apoptosis and inhibition of tumor growth. Inhibition of GADD45alpha and gamma in cancer cells by small interfering RNA abrogates apoptosis induction by the inhibitor of NF-kappaB and blocks c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation, whereas overexpression of GADD45alpha and gamma activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase and induces apoptosis. These results establish an unambiguous role for the GADD45 family as an essential mediator of cell survival in cancer cells with implications for cancer chemotherapy and novel drug discovery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contrasting roles of NF-kappaB and JNK in arsenite-induced p53-independent expression of GADD45alpha.Oncogene. 2001 Jun 14;20(27):3585-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204442. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11429707
-
Life and death in cancer. GADD45 alpha and gamma are critical regulators of NF-kappaB mediated escape from programmed cell death.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jan;4(1):18-20. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.1.1363. Epub 2005 Jan 11. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15613850
-
Gadd45 proteins as critical signal transducers linking NF-kappaB to MAPK cascades.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009 Dec;9(8):915-30. doi: 10.2174/156800909790192383. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 20025601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient activation of NF-kappaB through a TAK1/IKK kinase pathway by TGF-beta1 inhibits AP-1/SMAD signaling and apoptosis: implications in liver tumor formation.Oncogene. 2003 Jan 23;22(3):412-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206132. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12545162
-
GADD45 proteins: central players in tumorigenesis.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Jun;12(5):634-51. doi: 10.2174/156652412800619978. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22515981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The RUNX1 transcription factor is expressed in serous epithelial ovarian carcinoma and contributes to cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Cell Cycle. 2013 Mar 15;12(6):972-86. doi: 10.4161/cc.23963. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23442798 Free PMC article.
-
IKKbeta programs to turn on the GADD45alpha-MKK4-JNK apoptotic cascade specifically via p50 NF-kappaB in arsenite response.J Cell Biol. 2006 Nov 20;175(4):607-17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200602149. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17116751 Free PMC article.
-
The stress granule protein G3BP1 recruits protein kinase R to promote multiple innate immune antiviral responses.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2575-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02791-14. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25520508 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd45g insufficiency drives the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 6;15(1):2989. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47297-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38582902 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Xanthatin as a Killer of Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Mammosphere Cells: A Comparative Study with Salinomycin.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Aug 25;44(9):3849-3858. doi: 10.3390/cimb44090264. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36135176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li, Q. & Verma, I. M. (2002) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 725–734. - PubMed
-
- Karin, M., Cao, Y., Greten, F. R. & Li, Z. W. (2002) Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 301–310. - PubMed
-
- Zerbini, L. F., Wang, Y., Cho, J. Y. & Libermann, T. A. (2003) Cancer Res. 63, 2206–2215. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan, D., Uchiyama, H., Akbarali, Y., Urashima, M., Yamamoto, K., Libermann, T. A. & Anderson, K. C. (1996) Blood 87, 1104–1112. - PubMed
-
- Oya, M., Takayanagi, A., Horiguchi, A., Mizuno, R., Ohtsubo, M., Marumo, K., Shimizu, N. & Murai, M. (2003) Carcinogenesis 24, 377–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

