Activation of apoptosis in vivo by a hydrocarbon-stapled BH3 helix
- PMID: 15353804
- PMCID: PMC1360987
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1099191
Activation of apoptosis in vivo by a hydrocarbon-stapled BH3 helix
Abstract
BCL-2 family proteins constitute a critical control point for the regulation of apoptosis. Protein interaction between BCL-2 members is a prominent mechanism of control and is mediated through the amphipathic alpha-helical BH3 segment, an essential death domain. We used a chemical strategy, termed hydrocarbon stapling, to generate BH3 peptides with improved pharmacologic properties. The stapled peptides, called "stabilized alpha-helix of BCL-2 domains" (SAHBs), proved to be helical, protease-resistant, and cell-permeable molecules that bound with increased affinity to multidomain BCL-2 member pockets. A SAHB of the BH3 domain from the BID protein specifically activated the apoptotic pathway to kill leukemia cells. In addition, SAHB effectively inhibited the growth of human leukemia xenografts in vivo. Hydrocarbon stapling of native peptides may provide a useful strategy for experimental and therapeutic modulation of protein-protein interactions in many signaling pathways.
Figures

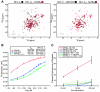
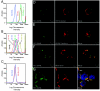
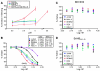
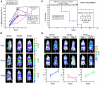
Comment in
-
Medicine. Targeting apoptotic pathways in cancer cells.Science. 2004 Sep 3;305(5689):1411-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1102974. Science. 2004. PMID: 15353788 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

