Comparison of glucose tolerance in renal transplant recipients and hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 15355547
- PMCID: PMC522749
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-5-11
Comparison of glucose tolerance in renal transplant recipients and hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Impaired glucose tolerance is a risk factor for atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients and renal transplant recipients.
Methods: To check the relationship of impaired glucose tolerance with the other atherosclerotic risk factors, fasting blood sugar and the standard two hour glucose tolerance test, serum tryglyceride, serum cholesterol, cyclosporine through level (in renal transplant recipients) and hemoglobin A1C were measured in 55 stable renal transplant recipients, 55 hemodialysis patients and 55 healthy controls with similar demographic characteristics. Patients with diabetes mellitus and propranolol consumers were excluded. The mean age and female to male ratio were 39 +/- 7 years and 23/22, respectively.
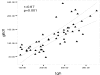
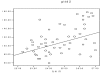
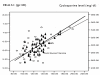
Results: Four of the renal transplant recipients and twelve of the hemodialysis patients had impaired glucose tolerance. Significant linear correlation was observed with body mass index and IGT only in hemodialysis patients (r = 0.4, p = 0.05). Glucose tolerance also had a significant correlation with triglyceride levels (217.2 +/- 55 mg/dl in hemodialysis patients vs. 214.3 +/- 13 mg/dl in renal transplant recipients and 100.2 +/- 18 mg/dl in control groups, p = 0.001). The glucose tolerance had significant relationship with higher serum cholesterol levels only in the renal transplant recipients (269.7 +/- 54 in renal transplant recipients vs. 199.2 +/- 36.6 mg/dl in hemodialysis and 190.5 +/- 34 mg/dl in control groups, p = 0.0001). In the renal transplant recipients, a linear correlation was observed with glucose tolerance and both the serum cyclosporine level (r = 0.9, p = 0.001) and the hemoglobin A1C concentration (6.2 +/- 0.9 g/dl). The later correlation was also observed in the hemodialysis patients (6.4 +/- 0.7 g/dl; r = 67, p = 0.001).
Conclusions: We conclude that although fasting blood sugar is normal in non-diabetic renal transplant and hemodialysis patients, impaired glucose tolerance could be associated with the other atherosclerotic risk factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unmasking glucose metabolism alterations in stable renal transplant recipients: a multicenter study.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 May;3(3):808-13. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04921107. Epub 2008 Mar 5. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18322043 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transplant hyperglycaemia: a study of risk factors.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003 Jan;18(1):164-71. doi: 10.1093/ndt/18.1.164. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003. PMID: 12480976
-
Abnormal glucose metabolism and metabolic syndrome in non-diabetic kidney transplant recipients early after transplantation.Transplantation. 2010 Apr 27;89(8):1034-9. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181d05a90. Transplantation. 2010. PMID: 20130496 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion from Tacrolimus to Cyclosporine A Improves Glucose Tolerance in HCV-Positive Renal Transplant Recipients.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 6;11(1):e0145319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145319. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26735686 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prevalence and risk factors of pre-diabetes after renal transplantation: a single-centre cohort study in 200 consecutive patients.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Aug;27(8):3330-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs020. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22492827
Cited by
-
The frequency of prediabetes and contributing factors in patients with chronic kidney disease.Rev Diabet Stud. 2011 Summer;8(2):276-81. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2011.8.276. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Rev Diabet Stud. 2011. PMID: 22189551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joy MS, Cefalu WT, Hogan SL, Nachman PH. Long-term glycemic control measurements in diabetic patients receiving hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39:297–307. - PubMed
-
- Mak RH, DeFronzo RA. Glucose and insulin metabolism in uremia. Nephron. 1992;61:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Androgue HJ. Glucose hemostasis and the kidney. Kidney Int. 1992;42:1266–1282. - PubMed
-
- Alverstrand A. Carbohydrate and insulin metabolism in renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997;52:S48–S52. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz O. Insulin mediated glucose uptake in nondialysed and dialysed uremic insulin dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1985;34:1152–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

