Iterative class discovery and feature selection using Minimal Spanning Trees
- PMID: 15355552
- PMCID: PMC520744
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-126
Iterative class discovery and feature selection using Minimal Spanning Trees
Abstract
Background: Clustering is one of the most commonly used methods for discovering hidden structure in microarray gene expression data. Most current methods for clustering samples are based on distance metrics utilizing all genes. This has the effect of obscuring clustering in samples that may be evident only when looking at a subset of genes, because noise from irrelevant genes dominates the signal from the relevant genes in the distance calculation.
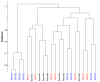
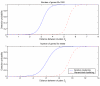
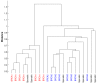
Results: We describe an algorithm for automatically detecting clusters of samples that are discernable only in a subset of genes. We use iteration between Minimal Spanning Tree based clustering and feature selection to remove noise genes in a step-wise manner while simultaneously sharpening the clustering. Evaluation of this algorithm on synthetic data shows that it resolves planted clusters with high accuracy in spite of noise and the presence of other clusters. It also shows a low probability of detecting spurious clusters. Testing the algorithm on some well known micro-array data-sets reveals known biological classes as well as novel clusters.
Conclusions: The iterative clustering method offers considerable improvement over clustering in all genes. This method can be used to discover partitions and their biological significance can be determined by comparing with clinical correlates and gene annotations. The MATLAB programs for the iterative clustering algorithm are available from http://linus.nci.nih.gov/supplement.html
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA microarray data and contextual analysis of correlation graphs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2003 Apr 29;4:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-15. Epub 2003 Apr 29. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12720549 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized maps for assessing the reliability of patients clusters in DNA microarray data analyses.Artif Intell Med. 2006 Jun;37(2):85-109. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2006.03.005. Epub 2006 May 23. Artif Intell Med. 2006. PMID: 16720093
-
Cluster stability scores for microarray data in cancer studies.BMC Bioinformatics. 2003 Sep 6;4:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-36. Epub 2003 Sep 6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12959646 Free PMC article.
-
Primer on medical genomics. Part III: Microarray experiments and data analysis.Mayo Clin Proc. 2002 Sep;77(9):927-40. doi: 10.4065/77.9.927. Mayo Clin Proc. 2002. PMID: 12233926 Review.
-
Genomic approaches to the pathogenesis of hematologic malignancy.Curr Opin Hematol. 2001 Jul;8(4):252-61. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200107000-00012. Curr Opin Hematol. 2001. PMID: 11561164 Review.
Cited by
-
HAMSTER: visualizing microarray experiments as a set of minimum spanning trees.Source Code Biol Med. 2009 Nov 20;4:8. doi: 10.1186/1751-0473-4-8. Source Code Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 19925686 Free PMC article.
-
A unified computational model for revealing and predicting subtle subtypes of cancers.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 May 1;13:70. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-70. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22548981 Free PMC article.
-
Individualized markers optimize class prediction of microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Jul 14;7:345. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-345. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16842618 Free PMC article.
-
Similarity searches in genome-wide numerical data sets.Biol Direct. 2006 May 30;1:13. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-1-13. Biol Direct. 2006. PMID: 16734895 Free PMC article.
-
A novel strategy for gene selection of microarray data based on gene-to-class sensitivity information.PLoS One. 2014 May 20;9(5):e97530. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097530. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24844313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J, Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. doi: 10.1038/35000501. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lapointe J, Li C, Higgins JP, van de Rijn M, Bair E, Montgomery K, Ferrari M, Egevad L, Rayford W, Bergerheim U, Ekman P, DeMarzo AM, Tibshirani R, Botstein D, Brown PO, Brooks JD, Pollack JR. Gene expression profiling identifies clinically relevant subtypes of prostate cancer. PNAS. 2004;101:811–816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0304146101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Seftor E, Hendrix M, Radmacher M, Simon R, Yakhini Z, Ben-Dor A, Sampas N, Dougherty E, Wang E, Marincola F, Gooden C, Lueders J, Glatfelter A, Pollock P, Carpten J, Gillanders E, Leja D, Dietrich K, Beaudry C, Berens M, Alberts D, Sondak V. Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;406:536–40. doi: 10.1038/35020115. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

