Developmental regulation of nicotinic synapses on cochlear inner hair cells
- PMID: 15356192
- PMCID: PMC6729925
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2102-04.2004
Developmental regulation of nicotinic synapses on cochlear inner hair cells
Abstract
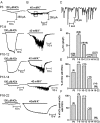
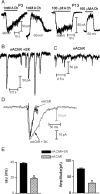
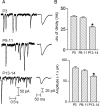
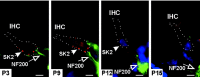
In the mature cochlea, inner hair cells (IHCs) transduce acoustic signals into receptor potentials, communicating to the brain by synaptic contacts with afferent fibers. Before the onset of hearing, a transient efferent innervation is found on IHCs, mediated by a nicotinic cholinergic receptor that may contain both alpha9 and alpha10 subunits. Calcium influx through that receptor activates calcium-dependent (SK2-containing) potassium channels. This inhibitory synapse is thought to disappear after the onset of hearing [after postnatal day 12 (P12)]. We documented this developmental transition using whole-cell recordings from IHCs in apical turns of the rat organ of Corti. Acetylcholine elicited ionic currents in 88-100% of IHCs between P3 and P14, but in only 1 of 11 IHCs at P16-P22. Potassium depolarization of efferent terminals caused IPSCs in 67% of IHCs at P3, in 100% at P7-P9, in 93% at P10-P12, but in only 40% at P13-P14 and in none of the IHCs tested between P16 and P22. Earlier work had shown by in situ hybridization that alpha9 mRNA is expressed in adult IHCs but that alpha10 mRNA disappears after the onset of hearing. In the present study, antibodies to alpha10 and to the associated calcium-dependent (SK2) potassium channel showed a similar developmental loss. The correlated expression of these gene products with functional innervation suggests that Alpha10 and SK2, but not Alpha9, are regulated by synaptic activity. Furthermore, this developmental knock-out of alpha10, but not alpha9, supports the hypothesis that functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in hair cells are heteromers containing both these subunits.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Constitutive expression of the alpha10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit fails to maintain cholinergic responses in inner hair cells after the onset of hearing.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2009 Sep;10(3):397-406. doi: 10.1007/s10162-009-0173-z. Epub 2009 May 19. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2009. PMID: 19452222 Free PMC article.
-
Onset of cholinergic efferent synaptic function in sensory hair cells of the rat cochlea.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19;31(42):15092-101. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2743-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22016543 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the expression and role of the α1-nAChR subunit in efferent cholinergic function during the development of the mammalian cochlea.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Aug 1;116(2):479-92. doi: 10.1152/jn.01038.2015. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27098031 Free PMC article.
-
How to build an inner hair cell: challenges for regeneration.Hear Res. 2007 May;227(1-2):3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2006.12.005. Epub 2006 Dec 16. Hear Res. 2007. PMID: 17258412 Review.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor structure and function in the efferent auditory system.Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2006 Apr;288(4):424-34. doi: 10.1002/ar.a.20302. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16550589 Review.
Cited by
-
Hair cells--beyond the transducer.J Membr Biol. 2006 Feb-Mar;209(2-3):89-118. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0835-7. Epub 2006 May 25. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16773496 Review.
-
Genetic deletion of SK2 channels in mouse inner hair cells prevents the developmental linearization in the Ca2+ dependence of exocytosis.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 1;583(Pt 2):631-46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.136630. Epub 2007 Jul 12. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17627990 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitating efferent inhibition of inner hair cells in the cochlea of the neonatal rat.J Physiol. 2005 Jul 1;566(Pt 1):49-59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.087460. Epub 2005 May 5. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15878942 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal expression patterns of nicotinic acetylcholine α9 and α10 subunits in the embryonic and early postnatal inner ear.Neuroscience. 2011 Oct 27;194:326-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21843604 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated calcium signalling in cochlear sensory and non-sensory cells refines afferent innervation of outer hair cells.EMBO J. 2019 May 2;38(9):e99839. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899839. Epub 2019 Feb 25. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 30804003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C, LeBlanc C, Bobbin RP (1996) Differences in cholinergic responses from outer hair cells of rat and guinea pig. Hear Res 98: 9-17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
