Functional properties of motoneurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 15356197
- PMCID: PMC6729934
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1972-04.2004
Functional properties of motoneurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
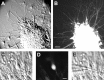
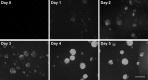
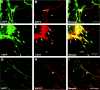
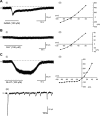
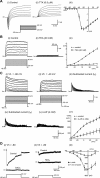
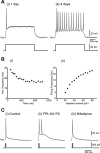
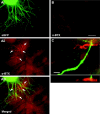
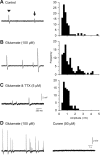
The capacity of embryonic stem (ES) cells to form functional motoneurons (MNs) and appropriate connections with muscle was investigated in vitro. ES cells were obtained from a transgenic mouse line in which the gene for enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) is expressed under the control of the promotor of the MN specific homeobox gene Hb9. ES cells were exposed to retinoic acid (RA) and sonic hedgehog agonist (Hh-Ag1.3) to stimulate differentiation into MNs marked by expression of eGFP and the cholinergic transmitter synthetic enzyme choline acetyltransferase. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were made from eGFP-labeled cells to investigate the development of functional characteristics of MNs. In voltage-clamp mode, currents, including EPSCs, were recorded in response to exogenous applications of GABA, glycine, and glutamate. EGFP-labeled neurons also express voltage-activated ion channels including fast-inactivating Na(+) channels, delayed rectifier and I(A)-type K(+) channels, and Ca(2+) channels. Current-clamp recordings demonstrated that eGFP-positive neurons generate repetitive trains of action potentials and that l-type Ca(2+) channels mediate sustained depolarizations. When cocultured with a muscle cell line, clustering of acetylcholine receptors on muscle fibers adjacent to developing axons was seen. Intracellular recordings of muscle fibers adjacent to eGFP-positive axons revealed endplate potentials that increased in amplitude and frequency after glutamate application and were sensitive to TTX and curare. In summary, our findings demonstrate that MNs derived from ES cells develop appropriate transmitter receptors, intrinsic properties necessary for appropriate patterns of action potential firing and functional synapses with muscle fibers.
Figures
References
-
- Arber S, Han B, Mendelsohn M, Smith M, Jessell TM, Sockanathan S (1999) Requirement for the homeobox gene Hb9 in the consolidation of motor neuron identity. Neuron 23: 659-674. - PubMed
-
- Arenas E (2002) Stem cells in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res Bull 57: 795-808. - PubMed
-
- Bain G, Kitchens D, Yao M, Huettner JE, Gottlieb DI (1995) Embryonic stem cells express neuronal properties in vitro. Dev Biol 168: 342-357. - PubMed
-
- Baldissera F, Gustafsson B (1971) Regulation of repetitive firing in motoneurones by the afterhyperpolarization conductance. Brain Res 30: 431-434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
