Loss of flight and associated neuronal rhythmicity in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mutants of Drosophila
- PMID: 15356199
- PMCID: PMC1289272
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0656-04.2004
Loss of flight and associated neuronal rhythmicity in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mutants of Drosophila
Abstract
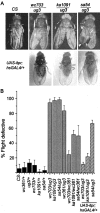
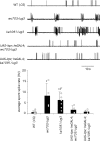
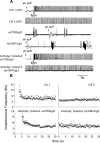
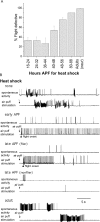
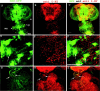
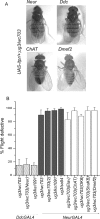
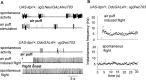
Coordinated flight in winged insects requires rhythmic activity of the underlying neural circuit. Here, we show that Drosophila mutants for the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP(3)) receptor gene (itpr) are flightless. Electrophysiological recordings from thoracic indirect flight muscles show increased spontaneous firing accompanied by a loss of rhythmic flight activity patterns normally generated in response to a gentle puff of air. In contrast, climbing speed, the jump response, and electrical properties of the giant fiber pathway are normal, indicating that general motor coordination and neuronal excitability are much less sensitive to itpr mutations. All mutant phenotypes are rescued by expression of an itpr(+) transgene in serotonin and dopamine neurons. Pharmacological and immunohistochemical experiments support the idea that the InsP(3) receptor functions to modulate flight specifically through serotonergic interneurons. InsP(3) receptor action appears to be important for normal development of the flight circuit and its central pattern generator.
Figures

References
-
- Aberle H, Haghighi AP, Fetter RD, McCabe BD, Magalhaes TR, Goodman CS (2002) Wishful thinking encodes a BMP type II receptor that regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila Neuron 33: 545-558. - PubMed
-
- Acharya JK, Jalink K, Hardy RW, Hartenstein V, Zuker CS (1997) InsP3 receptor is essential for growth and differentiation but not for vision in Drosophila Neuron 18: 881-887. - PubMed
-
- Baier A, Wittek B, Brembs B (2002) Drosophila as a new model organism for the neurobiology of aggression? J Exp Biol 205: 1233-1240. - PubMed
-
- Bainton RJ, Tsai LT, Singh CM, Moore MS, Neckameyer WS, Heberlein U (2000) Dopamine modulates acute responses to cocaine, nicotine and ethanol in Drosophila Curr Biol 10: 187-194. - PubMed
-
- Benzer S (1973) Genetic dissection of behavior. Sci Am 229: 24-37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
