Polyadenylation-dependent screening assay for respiratory syncytial virus RNA transcriptase activity and identification of an inhibitor
- PMID: 15356293
- PMCID: PMC519107
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh809
Polyadenylation-dependent screening assay for respiratory syncytial virus RNA transcriptase activity and identification of an inhibitor
Abstract
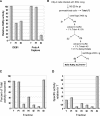
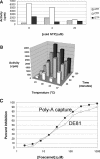
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a multi-subunit ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that, in addition to synthesizing the full 15 222 nt viral genomic RNA, is able to synthesize all 10 viral mRNAs. We have prepared crude RNP from RSV-infected HEp-2 cells, based on a method previously used for Newcastle disease virus, and established a novel polyadenylation-dependent capture [poly(A) capture] assay to screen for potential inhibitors of RSV transcriptase activity. In this homogeneous assay, radiolabeled full-length polyadenylated mRNAs produced by the viral RNP are detected through capture on immobilized biotinylated oligo(dT) in a 96-well streptavidin-coated FlashPlate. Possible inhibitors identified with this assay could interfere at any step required for the production of complete RSV mRNAs, including transcription, polyadenylation and, potentially, co-transcriptional guanylylation. A specific inhibitor of RSV transcriptase with antiviral activity was identified through screening of this assay.
Figures



References
-
- Collins P.L., Chanock,R.M. and Murphy,B.R. (2001) Respiratory syncytial virus. In Knipe,D.M.H.P.M. (ed.), Fields Virology. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkens, NY, pp. 1443–1485.
-
- Hall C.B., McBride,J.T., Walsh,E.E., Bell,D.M., Gala,C.L., Hildreth,S., Ten Eyck,L.G. and Hall,W.J. (1983) Aerosolized ribavirin treatment of infants with respiratory syncytial viral infection. A randomized double-blind study. N. Engl. J. Med., 308, 1443–1447. - PubMed
-
- Prince G.A. (2001) An update on respiratory syncytial virus antiviral agents. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs, 10, 297–308. - PubMed
-
- Groothuis J.R. and Nishida,H. (2002) Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infections in high-risk infants by monoclonal antibody (palivizumab). Pediatr. Int., 44, 235–241. - PubMed
-
- Prince A.M. and Jacobs,R.F. (2001) Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection in high risk infants. J. Ark. Med. Soc., 98, 115–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

