Structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5
- PMID: 15356295
- PMCID: PMC519115
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh824
Structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5
Abstract
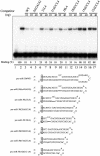
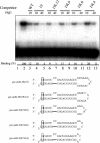
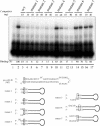
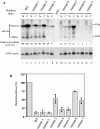
The biogenesis and function of mature human microRNAs is dependent on the nuclear export of pre-microRNA precursors by Exportin 5 (Exp5). The precursor for the human miR-30 microRNA, which is a 63 nt long RNA hairpin bearing a 2 nt 3' overhang, forms a specific complex with Exp5 and the Ran-GTP cofactor. Here, we have examined the structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding by Exp5. Our data indicate that pre-miR-30 binding requires an RNA stem of >16 bp and is facilitated by a 3' overhang. Although a blunt-ended derivative of the pre-miR-30 stem-loop remained capable of binding Exp5, 5' overhangs were inhibitory. miR-30 variants that had lost the ability to bind Exp5 effectively were not efficiently exported from the nucleus and were also expressed at reduced levels. Furthermore, formation of a pre-microRNA/Exp5/Ran-GTP complex inhibited exonucleolytic digestion of the pre-miRNA in vitro. Together, these data demonstrate that pre-microRNA binding by Exp5 involves recognition of almost all of the RNA hairpin, with the exception of the terminal loop. Moreover, these results argue that Exp5 binding not only mediates pre-microRNA nuclear export but also prevents nuclear pre-microRNA degradation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs.Genes Dev. 2003 Dec 15;17(24):3011-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.1158803. Epub 2003 Dec 17. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14681208 Free PMC article.
-
Selectivity of Exportin 5 binding to human precursor microRNAs.RNA Biol. 2021 Nov 12;18(sup2):730-737. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1984096. Epub 2021 Sep 30. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34592896 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic mechanisms for pre-miRNA binding and export by Exportin-5.RNA. 2011 Aug;17(8):1511-28. doi: 10.1261/rna.2732611. Epub 2011 Jun 28. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21712399 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA precursors in motion: exportin-5 mediates their nuclear export.Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;14(4):156-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.02.006. Trends Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15134074 Review.
-
Exportin t and Exportin 5: tRNA and miRNA biogenesis - and beyond.Biol Chem. 2012 Jul;393(7):599-604. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0146. Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22944664 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA interference is responsible for reduction of transgene expression after Sleeping Beauty transposase mediated somatic integration.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035389. Epub 2012 May 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22570690 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(17):5944-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm641. Epub 2007 Aug 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17726050 Free PMC article.
-
RDMAS: a web server for RNA deleterious mutation analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Sep 6;7:404. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-404. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16956394 Free PMC article.
-
Association of microRNA biosynthesis genes XPO5 and RAN polymorphisms with cancer susceptibility: Bayesian hierarchical meta-analysis.J Cancer. 2020 Feb 3;11(8):2181-2191. doi: 10.7150/jca.37150. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32127945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mature miRNAs form secondary structure, which suggests their function beyond RISC.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 25;9(11):e113848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113848. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25423301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel D.P. (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 116, 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y., Ahn,C., Han,J., Choi,H., Kim,J., Yim,J., Lee,J., Provost,P., Rådmark,O., Kim,S. and Kim,V.N. (2003) The nuclear RNase III drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature, 425, 415–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

