Structural characterization of Escherichia coli sensor histidine kinase EnvZ: the periplasmic C-terminal core domain is critical for homodimerization
- PMID: 15357641
- PMCID: PMC1134694
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041125
Structural characterization of Escherichia coli sensor histidine kinase EnvZ: the periplasmic C-terminal core domain is critical for homodimerization
Abstract
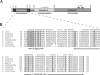
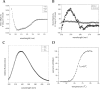
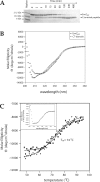
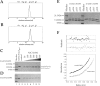
Escherichia coli EnvZ is a membrane sensor histidine kinase that plays a pivotal role in cell adaptation to changes in extracellular osmolarity. Although the cytoplasmic histidine kinase domain of EnvZ has been extensively studied, both biochemically and structurally, little is known about the structure of its periplasmic domain, which has been implicated in the mechanism underlying its osmosensing function. In the present study, we report the biochemical and biophysical characterization of the periplasmic region of EnvZ (Ala38-Arg162). This region was found to form a dimer in solution, and to consist of two well-defined domains: an N-terminal a-helical domain and a C-terminal core domain (Glu83-Arg162) containing both a-helical and b-sheet secondary structures. Our pull-down assays and analytical ultracentrifugation analysis revealed that dimerization of the periplasmic region is highly sensitive to the presence of CHAPS, but relatively insensitive to salt concentration, thus suggesting the significance of hydrophobic interactions between the homodimeric subunits. Periplasmic homodimerization is mediated predominantly by the C-terminal core domain, while a regulatory function may be attributed mainly to the N-terminal a-helical domain, whose mutations have been shown previously to produce a high-osmolarity phenotype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional and structural characterization of EnvZ, an osmosensing histidine kinase of E. coli.Methods Enzymol. 2007;423:184-202. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)23008-3. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17609132
-
Structural and functional studies of the HAMP domain of EnvZ, an osmosensing transmembrane histidine kinase in Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 7;282(36):26401-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701342200. Epub 2007 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17635923
-
Probing catalytically essential domain orientation in histidine kinase EnvZ by targeted disulfide crosslinking.J Mol Biol. 2003 Apr 25;328(2):409-18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00275-4. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12691749
-
EnvZ/OmpR Two-Component Signaling: An Archetype System That Can Function Noncanonically.EcoSal Plus. 2020 Jan;9(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2019. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2019. EcoSal Plus. 2020. PMID: 32003321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane protein folding on the example of outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003 Aug;60(8):1547-58. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3170-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 14513830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determination of the physiological dimer interface of the PhoQ sensor domain.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 13;379(4):656-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.023. Epub 2008 Apr 16. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18468622 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of transmembrane cell-surface receptors via a common mechanism? The "rotation model".Bioessays. 2015 Sep;37(9):959-67. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500041. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26241732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered regulation of the OmpF porin by Fis in Escherichia coli during an evolution experiment and between B and K-12 strains.J Bacteriol. 2011 Jan;193(2):429-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.01341-10. Epub 2010 Nov 19. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21097626 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus perception in bacterial signal-transducing histidine kinases.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Dec;70(4):910-38. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00020-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 17158704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the genetic components of adaptation of Escherichia coli to the mouse gut.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jan;4(1):e2. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040002. Epub 2007 Nov 27. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18193944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mizuno T. His-Asp phosphotransfer signal transduction. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1998;123:555–563. - PubMed
-
- West A. H., Stock A. M. Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001;26:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Mizuno T., Wurtzel E. T., Inouye M. Osmoregulation of gene expression. II. DNA sequence of the envZ gene of the ompB operon of Escherichia coli and characterization of its gene product. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257:13692–13698. - PubMed
-
- Forst S., Comeau D., Norioka S., Inouye M. Localization and membrane topology of EnvZ, a protein involved in osmoregulation of OmpF and OmpC in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:16433–16438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

