Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: an immunohistochemical study of 11 cases
- PMID: 15357873
- PMCID: PMC517938
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-4-11
Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: an immunohistochemical study of 11 cases
Abstract
Background: Collecting duct carcinoma (CDC) is a rare but very aggressive variant of kidney carcinoma that arises from the epithelium of Bellini's ducts, in the distal portion of the nephron. In order to gain an insight into the biology of this tumor we evaluated the expression of five genes involved in the development of renal cancer (FEZ1/LZTS1, FHIT, TP53, P27kip1, and BCL2).
Methods: We studied eleven patients who underwent radical nephrectomy for primary CDC. All patients had an adequate clinical follow-up and none of them received any systemic therapy before surgery. The expression of the five markers for tumor initiation and/or progression were assessed by immunohistochemistry and correlated to the clinicopathological parameters, and survival by univariate analysis.
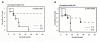
Results: Results showed that Fez1 protein expression was undetectable or substantially reduced in 7 of the 11 (64%) cases. Fhit protein was absent in three cases (27%). The overexpression of p53 protein was predominantly nuclear and detected in 4 of 11 cases (36%). Immunostaining for p27 was absent in 5 of 11 cases (45.5%). Five of the six remaining cases (90%) showed exclusively cytoplasmic protein expression, where, in the last case, p27 protein was detected in both nucleus and cytoplasm. Bcl2 expression with 100% of the tumor cells positive was observed in 4 of 11 (36%) cases. Statistical analysis showed a statistical trend (P = 0.06) between loss and reduction of Fez1 and presence of lymph node metastases.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that Fez1 may represent not only a molecular diagnostic marker but also a prognostic marker in CDC.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:8–29. - PubMed
-
- Holthofer H, Miettinen A, Paasivuo R, Lehto VP, Linder E, Alfthan O, Virtanen I. Cellular origin and differentiation of renal carcinomas. A fluorescence microscopic study with kidney-specific antibodies, antiintermediate filament antibodies, and lectins. Lab Invest. 1983;49:317–326. - PubMed
-
- Fleming S, Lewi HJ. Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney. Histopathology. 1986;10:1131–1141. - PubMed
-
- Peyromaure M, Thiounn N, Scotte F, Vieillefond A, Debre B, Oudard S. Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: a clinicopathological study of 9 cases. J Urol. 2003;170:1138–1140. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000086616.40603.ad. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Logothetis CJ, Markowitz A, Sella A, Amato R, Ro J. Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney. Br J Urol. 1993;71:388–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

