Serological response to Pasteurella multocida NanH sialidase in persistently colonized rabbits
- PMID: 15358639
- PMCID: PMC515265
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.5.825-834.2004
Serological response to Pasteurella multocida NanH sialidase in persistently colonized rabbits
Abstract
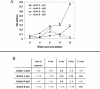
Pasteurella multocida is a mucosal pathogen that colonizes the upper respiratory system of rabbits. Respiratory infections can result, but the bacteria can also invade the circulatory system, producing abscesses or septicemia. P. multocida produces extracellular sialidase activity, which is believed to augment colonization of the respiratory tract and the production of lesions in an active infection. Previously, it was demonstrated that some isolates of P. multocida contain two unique sialidase genes, nanH and nanB, that encode enzymes with different substrate specificities (S. Mizan, A. D. Henk, A. Stallings, M. Meier, J. J. Maurer, and M. D. Lee, J. Bacteriol. 182:6874-6883, 2000). We developed a recombinant antigen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on the NanH sialidase of P. multocida and demonstrated that rabbits that were experimentally colonized with P. multocida produce detectable anti-NanH immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG in serum, although they demonstrated no clinical signs of pasteurellosis. In addition, clinically ill pet rabbits infected with P. multocida possessed IgM and/or IgG antibody against NanH. The NanH ELISA may be useful for the diagnosis of P. multocida infections in sick rabbits as well as for screening for carriers in research rabbit colonies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening rabbit colonies for antibodies to Pasteurella multocida by an ELISA.Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Oct;41(5):419-22. Lab Anim Sci. 1991. PMID: 1666140
-
Detection of antibodies against Pasteurella multocida using immunohistochemical staining in an outbreak of rabbit pasteurellosis.J Vet Med Sci. 2001 Feb;63(2):171-4. doi: 10.1292/jvms.63.171. J Vet Med Sci. 2001. PMID: 11258454
-
Cloning and characterization of sialidases with 2-6' and 2-3' sialyl lactose specificity from Pasteurella multocida.J Bacteriol. 2000 Dec;182(24):6874-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.24.6874-6883.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 11092845 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and typing options for investigating diseases associated with Pasteurella multocida.Vet Microbiol. 2008 Apr 1;128(1-2):1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.10.018. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Vet Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18061377 Review.
-
Pasteurella multocida and bovine respiratory disease.Anim Health Res Rev. 2007 Dec;8(2):129-50. doi: 10.1017/S1466252307001399. Anim Health Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 18218157 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative treatment of serious and mild Pasteurella multocida infection in New Zealand White rabbits.BMC Vet Res. 2014 Nov 25;10:276. doi: 10.1186/s12917-014-0276-6. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25420780 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory, Immunomodulatory, and Antioxidant Activities of Allicin, Norfloxacin, or Their Combination against Pasteurella multocida Infection in Male New Zealand Rabbits.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jun 27;2018:1780956. doi: 10.1155/2018/1780956. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30050645 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and purification of NanB sialidase from Pasteurella multocida with activity in hydrolyzing sialic acid Neu5Acα(2-6)Gal and Neu5Acα(2-3)Gal.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 8;12(1):9425. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13635-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35676312 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence Analysis and Characterization of Selected Iron Regulation Genes of Pasteurella Multocida Serotype A Strain PMTB2.1.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 25;10(2):81. doi: 10.3390/genes10020081. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30691021 Free PMC article.
-
Single level posterolateral lumbar fusion in a New Zealand White rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) model: Surgical anatomy, operative technique, autograft fusion rates, and perioperative care.JOR Spine. 2020 Dec 23;4(1):e1135. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1135. eCollection 2021 Mar. JOR Spine. 2020. PMID: 33778408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Haddawi, M. H., S. Jasni, M. Zamri-Saad, A. R. Mutalib, and A. R. Sheikh-Omar. 1999. Ultrastructural pathology of the upper respiratory tract of rabbits experimentally infected with Pasteurella multocida A:3. Res. Vet. Sci. 67:163-170. - PubMed
-
- Al-Haddawi, M. H., S. Jasni, M. Zamri-Saad, A. R. Mutalib, I. Zulkifli, R. Son, and A. R. Sheikh-Omar. 2000. In vitro study of Pasteurella multocida adhesion to trachea, lung and aorta of rabbits. Vet. J. 159:274-281. - PubMed
-
- Al-Haddawi, M. H., S. Jasni, D. A. Israf, M. Zamri-Saad, A. R. Mutalib, and A. R. Sheikh-Omar. 2001. Ultrastructural pathology of nasal and tracheal mucosa of rabbits experimentally infected with Pasteurella multocida serotype D:1. Res. Vet. Sci. 70:191-197. - PubMed
-
- Al-Lebban, Z. S., L. B. Corbeil, and E. H. Coles. 1988. Rabbit pasteurellosis: induced disease and vaccination. Am. J. Vet. Res. 49:312-316. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1993. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates Inc. and John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Boston, Mass.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

