A prospective study of pregnant patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis using validated clinical instruments
- PMID: 15361373
- PMCID: PMC1754757
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.016881
A prospective study of pregnant patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis using validated clinical instruments
Abstract
Objective: : To analyse the disease course of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) during and after pregnancy by validated clinical instruments for measurement of disease activity, and assess their usefulness in pregnant patients.
Methods: Included were 10 patients with RA and 9 with AS (10 pregnancies). Clinical examination and blood/urine sampling was performed before conception, at each trimester, and weeks 6, 12, and 24 post partum. Assessment of RA was by the RA Disease Activity Index (RADAI), the 44 joint count, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire; assessment of AS by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Activity Index (BASDAI), the Dougados Functional and Articular Index, and a night pain index. Common for all patients were the patient's and physician's global assessment.
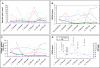
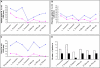
Results: : Most patients with RA showed sustained or increased improvement of disease activity during pregnancy. Higher disease activity scores were found in the patients with AS with a frequent increase of disease activity in the second trimester and mitigation of symptoms in the third trimester. Analysis specifically for the patient's assessment of pain showed continuously higher pain scores in the patients with AS than in those with RA. Rank correlation showed good to moderate correlation between most clinical measurements and RADAI or BASDAI, respectively. Functional indices were confounded by physiological changes of late pregnancy.
Conclusion: RA can be monitored during and after pregnancy by the swollen joint count and RADAI without interference from pregnancy related symptoms, whereas usual measures of disease activity are not always applicable in pregnant patients with AS.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

