Decrease of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor following anti-TNFalpha therapy (infliximab) in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with clinical improvement
- PMID: 15361374
- PMCID: PMC1754775
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.014647
Decrease of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor following anti-TNFalpha therapy (infliximab) in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with clinical improvement
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of infliximab treatment on anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (anti-CCP) and rheumatoid factor (RF) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: 43 patients with rheumatoid arthritis not responding to disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARD) received intravenous infliximab at a dose of 3 mg/kg at baseline and after two and six weeks, and subsequently bimonthly, in combination with methotrexate. Serum samples were collected at baseline and at week 24. A commercial enzyme linked immunosorbent assay was used to test for anti-CCP antibodies; RF were detected using a quantitative nephelometric assay.
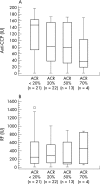
Results: At baseline, 38 of the 43 patients (88%) were positive for anti-CCP antibodies, and 41 (95%) were positive for RF. The serum titre of anti-CCP and RF decreased significantly after six months of treatment (p = 0.0001 and p<0.0001, respectively). When the patients were grouped on the basis of their clinical response to infliximab, a significant decrease in serum anti-CCP antibodies and RF was observed only in patients who had clinical improvement (ACR 20 and ACR 50).
Conclusions: Anti-TNFalpha treatment in rheumatoid arthritis results in a decrease in the serum titres of RF and anti-CCP antibodies in patients showing clinical improvement, suggesting that these measurements may be a useful adjunct in assessing treatment efficacy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Methotrexate effect on anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody levels in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Aug;64(8):1241-2. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.032136. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 16014691 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

