The hydrodynamic radii of macromolecules and their effect on red blood cell aggregation
- PMID: 15361408
- PMCID: PMC1304934
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.047746
The hydrodynamic radii of macromolecules and their effect on red blood cell aggregation
Abstract
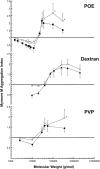
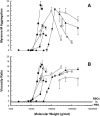
The effects of nonionic polymers on human red blood cell (RBC) aggregation were investigated. The hydrodynamic radius (Rh) of individual samples of dextran, polyvinylpyrrolidone, and polyoxyethylene over a range of molecular weights (1,500-2,000,000) were calculated from their intrinsic viscosities using the Einstein viscosity relation and directly measured by quasi-elastic light scattering, and the effect of each polymer sample on RBC aggregation was studied by nephelometry and low-shear viscometry. For all three polymers, despite their different structures, samples with Rh <4 nm were found to inhibit aggregation, whereas those with Rh >4 nm enhanced aggregation. Inhibition increased with Rh and was maximal at approximately 3 nm; above 4 nm the pro-aggregant effect increased with Rh. For comparison, the Rh of 12 plasma proteins were calculated from literature values of intrinsic viscosity or diffusion coefficient. Each protein known to promote RBC aggregation had Rh >4 nm, whereas those with Rh <4 nm either inhibited or had no effect on aggregation. These results suggest that the influence of a nonionic polymer or plasma protein on RBC aggregation is simply a consequence of its size in an aqueous environment, and that the specific type of macromolecule is of minor importance.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad, F., and P. McPhie. 1980. The intrinsic viscosity of glycoproteins. Int. J. Biochem. 11:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, J. K., H. J. Meiselman, and T. C. Fisher. 1999. Evidence against macromolecular “bridging” as the mechanism of red blood cell aggregation induced by nonionic polymers. Biorheology. 36:433–437. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, J. K., H. J. Meiselman, and T. C. Fisher. 2002. Red blood cell aggregation: the effect of nonionic polymers and the role of hydrodynamic root mean square radius of gyration. Biorheology. 39:611. (Abstr.)
-
- Arturson, G., K. Granath, L. Thorén, and G. Wallenius. 1964. The renal excretion of low molecular weight dextran. Acta Chir. Scand. 127:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Asakura, S., and F. Oosawa. 1954. On interaction between two bodies immersed in a solution of macromolecules. J. Chem. Phys. 22:1255–1256.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

