Ultrastructure of spermatozoa of Bullacta exarata (philippi) and its significance on reproductive evolution and physio-ecological adaptation
- PMID: 15362192
- PMCID: PMC1388726
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2004.1211
Ultrastructure of spermatozoa of Bullacta exarata (philippi) and its significance on reproductive evolution and physio-ecological adaptation
Abstract
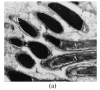
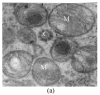
The morphology and ultrastructure of Bullacta exarata spermatozoa observed by light and transmission electron microscopy are presented in this paper. The spermatozoa is composed of head with a simple acrosomal complex and an elongated nucleus, and tail with a midpiece, principal piece and an end piece. The midpiece consists of a mitochondrial ring, and the principal piece is composed of axoneme and lateral fin. The structure of B. exarata spermatozoa differs significantly from that of other gastropods, especially in the lateral fin and the principal piece, which was described scarcely before. A comparison is made between B. exarata and other gastropods, and its significance on reproductive evolution and physio-ecological adaptation is preliminarily discussed.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Ultrastructure of the spermatozoa of Cicadella viridis (Linnaeus) and its bearing on the phylogeny of Auchenorrhyncha.Micron. 2012 Sep;43(9):978-84. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2012.03.022. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Micron. 2012. PMID: 22503399
-
Sperm ultrastructure in the nudibranch genus Halgerda with reference to other Discodorididae and to Chromodorididae (Mollusca: Opisthobranchia).J Morphol. 2003 Jul;257(1):9-21. doi: 10.1002/jmor.10086. J Morphol. 2003. PMID: 12740892
-
Ultrastructure of the sperm and spermatogenesis in five South African species of the trochid genus Oxystele (Mollusca, Prosobranchia).Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Mar;25(3):263-71. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080250308. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990. PMID: 2331375
-
The evolution of the sperm tail.Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:521-32. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982. PMID: 6223401 Review.
-
Ultra-imaging in applied animal andrology: The power and the beauty.Anim Reprod Sci. 2020 Sep;220:106306. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2020.106306. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Anim Reprod Sci. 2020. PMID: 32085922 Review.
Cited by
-
A chromosome-level genome assembly of the Bullacta exarata (Cephalaspidea: Haminoeidae).Sci Data. 2025 Jun 16;12(1):1008. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05373-2. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40523891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao ZM, Hu JJ, Jiang M, Liu XY. Ultrastructure of the spermatozoa of the Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao. 1998;28(2):283–287. (in Chinese)
-
- Bojat NC, Sauder U, Haase M. The spermathecal epithelium, sperm and their interactions in the hermaphroditic land snail Arianta arbustorum (Pulmonata, Stylommatophoral) Zoomorphology. 2001;120:149–157.
-
- Buckland-Nicks J, Howley B. Spermiogenesis and sperm structure in relation to early events of fertilization in the Limpet Tectura testudinalis (Müller) Biol. Bull. 1997;193:306–319. - PubMed
-
- Franzen A. Ultrastructural studies of spermatozoa in three bivalvia species with notes on evolution of elongated sperm nucleus in primitive spermatozoa. Gamete Res. 1983;7:199–214.
-
- Healy JM. Electron microscopic observations on the spermatozoa of a marine pulmonate slug, Onchidium damcllii (Gastropoda, Onchidiacea) J. Submicrosc. Cyto. 1986;18(3):587–594.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

