IL-6 plays an obligatory role in late preconditioning via JAK-STAT signaling and upregulation of iNOS and COX-2
- PMID: 15364614
- PMCID: PMC3691700
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.05.011
IL-6 plays an obligatory role in late preconditioning via JAK-STAT signaling and upregulation of iNOS and COX-2
Abstract
Objective: We sought to determine whether interleukin (IL)-6 modulates myocardial infarction or the late phase of preconditioning (PC).
Methods: Wild-type and IL-6(-/-) mice underwent a 30-min coronary occlusion followed by 24 h of reperfusion with or without six cycles of coronary occlusion/reperfusion 24 h earlier. Myocardial IL-6 protein expression, activation of Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2, and signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 after ischemic PC protocol were examined. The expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 was determined 24 h after the PC ischemia.
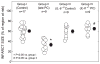
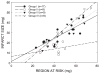
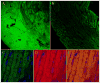
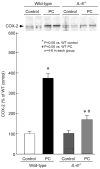
Results: In preconditioned wild-type mice, infarct size was reduced from 60.5+/-2.6% of the risk region to 33.5+/-3.6%, indicating a late PC effect. In nonpreconditioned IL-6(-/-) mice, infarct size was similar to that observed in wild-type mice (59.9+/-3.8%), indicating that the deletion of IL-6 has no effect on infarct size. However, in preconditioned IL-6(-/-) mice, infarct size was not reduced (65.1+/-3.1%), indicating that the infarct-sparing effect was completely abrogated. Ischemic PC increased the expression of IL-6 in the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes in the ischemic/reperfused zone. In IL-6(-/-) mice, the ischemic PC-induced activation of JAK1 and JAK2 and STAT1 and STAT3 was significantly reduced, and the increase in iNOS and COX-2 protein expression 24 h after the PC ischemia was markedly attenuated.
Conclusion: IL-6 does not modulate myocardial infarct size in naïve myocardium. However, following a PC stimulus, IL-6 is obligatorily required for the activation of the JAK-STAT pathway, the ensuing upregulation of iNOS and COX-2 (co-mediators of late PC), and the development of a cardioprotective phenotype.
Figures




Comment in
-
Cytokines and late preconditioning.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 Oct 1;64(1):6-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.07.019. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15364607 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of cyclooxygenase-2 upregulation in late preconditioning.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003 May;35(5):525-37. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(03)00076-2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12738234 Free PMC article.
-
An essential role of the JAK-STAT pathway in ischemic preconditioning.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jul 31;98(16):9050-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161283798. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11481471 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase plays an obligatory role in the late phase of ischemic preconditioning by activating the protein kinase C epsilon p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase pSer-signal transducers and activators of transcription1/3 pathway.Circulation. 2007 Jul 31;116(5):535-44. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.689471. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17606840 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2003 Feb;13(2):72-9. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(02)00230-x. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2003. PMID: 12586443 Review.
-
Discovery of a new function of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: COX-2 is a cardioprotective protein that alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury and mediates the late phase of preconditioning.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Aug 15;55(3):506-19. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00414-5. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 12160947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of the innate immune NLRP3 receptor abolishes cardiac ischemic preconditioning and is associated with decreased Il-6/STAT3 signaling.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040643. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848390 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Dec;53(6):858-69. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.09.007. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22999860 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Colitic Effects of Ethanol Extract of Persea americana Mill. through Suppression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators via NF-κB/STAT3 Inactivation in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 5;20(1):177. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010177. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30621304 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory processes in cardiovascular disease: a route to targeted therapies.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017 Mar;14(3):133-144. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.185. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27905474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin Mediates Cardiac Tissue Damage under Septic Conditions Induced by Lipopolysaccharide.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 15;25(20):11088. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011088. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuzuya T, Hoshida S, Yamashita N, et al. Delayed effects of sublethal ischemia on the acquisition of tolerance to ischemia. Circ Res. 1993;72:1293–9. - PubMed
-
- Bolli R. The late phase of preconditioning. Circ Res. 2000;87:972–83. - PubMed
-
- Yellon DM, Downey JM. Preconditioning the myocardium: from cellular physiology to clinical cardiology. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1113–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-65660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-68088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043151/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-70897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-43151/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072410/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-55757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-72410/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

