Differing patterns of liver disease progression and hepatitis C virus (HCV) quasispecies evolution in children vertically coinfected with HCV and human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 15365046
- PMCID: PMC516277
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.9.4365-4369.2004
Differing patterns of liver disease progression and hepatitis C virus (HCV) quasispecies evolution in children vertically coinfected with HCV and human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
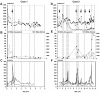
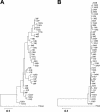
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) quasispeciation was studied in two children vertically coinfected with HCV and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). HCV quasispecies diversification and liver injury were more significant in patient C1, who was immunocompetent with anti-HIV therapy, than in patient C2, who was immunosuppressed, in consistency with modulation of HCV quasispeciation and liver injury by immunocompetence in coinfected children.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective study of mother-to-infant transmission of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Study Group for Vertical Transmission.J Med Virol. 1998 Jan;54(1):12-9. J Med Virol. 1998. PMID: 9443104
-
Slow progression of human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus disease in a cohort of coinfected children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007 Sep;26(9):846-9. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318123e8e6. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007. PMID: 17721385
-
Impact of human immunodeficiency virus coinfection on the progression of mother-to-child transmitted hepatitis C virus infection.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011 Sep;30(9):801-4. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182196ab4. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011. PMID: 21772231
-
Mother-to-infant transmission of hepatitis C virus.Clin Invest Med. 1996 Oct;19(5):368-72. Clin Invest Med. 1996. PMID: 8889276 Review.
-
Role of liver biopsy in the evaluation of hepatitis C virus infection in HIV coinfection.Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Apr 15;40 Suppl 5:S270-5. doi: 10.1086/427439. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15768334 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C virus quasispecies in chronically infected children subjected to interferon-ribavirin therapy.Arch Virol. 2010 Dec;155(12):1977-87. doi: 10.1007/s00705-010-0789-7. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Arch Virol. 2010. PMID: 20842394 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus molecular evolution: transmission, disease progression and antiviral therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 21;20(43):15992-6013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.15992. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25473152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The quasispecies nature and biological implications of the hepatitis C virus.Infect Genet Evol. 2009 Dec;9(6):1158-67. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.07.011. Epub 2009 Aug 8. Infect Genet Evol. 2009. PMID: 19666142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vertical Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus: Variable Transmission Bottleneck and Evidence of Midgestation In Utero Infection.J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e01372-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01372-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28931691 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of hepatitis C during pregnancy and childhood.Viruses. 2012 Dec 6;4(12):3531-50. doi: 10.3390/v4123531. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23223189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badizadegan, K., M. M. Jonas, M. J. Ott, S. P. Nelson, and A. R. Perez-Atayde. 1998. Histopathology of the liver in children with chronic hepatitis C viral infection. Hepatology 28:1416-1423. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1994. 1994 revised classification system for human immunodeficiency virus infection in children less than 13 years of age. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 43(RR-12):1-11.
-
- Cerny, A., and F. V. Chisari. 1999. Pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C: immunological features of hepatic injury and viral persistence. Hepatology 30:595-601. - PubMed
-
- Cribier, B., D. Rey, C. Schmitt, J. M. Lang, A. Kirn, and F. Stoll-Keller. 1995. High hepatitis C viraemia and impaired antibody response in patients coinfected with HIV. AIDS 9:1131-1136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

