The functional basis for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with co-inherited missense mutations in the perforin (PFN1) gene
- PMID: 15365097
- PMCID: PMC2211966
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040776
The functional basis for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with co-inherited missense mutations in the perforin (PFN1) gene
Abstract
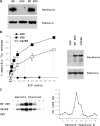
About 30% of cases of the autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis are believed to be caused by inactivating mutations of the perforin gene. We expressed perforin in rat basophil leukemia cells to define the basis of perforin dysfunction associated with two mutations, R225W and G429E, inherited by a compound heterozygote patient. Whereas RBL cells expressing wild-type perforin (67 kD) efficiently killed Jurkat target cells to which they were conjugated, the substitution to tryptophan at position 225 resulted in expression of a truncated ( approximately 45 kD) form of the protein, complete loss of cytotoxicity, and failure to traffic to rat basophil leukemia secretory granules. By contrast, G429E perforin was correctly processed, stored, and released, but the rat basophil leukemia cells possessed reduced cytotoxicity. The defective function of G429E perforin mapped downstream of exocytosis and was due to its reduced ability to bind lipid membranes in a calcium-dependent manner. This study elucidates the cellular basis for perforin dysfunctions in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and provides the means for studying structure-function relationships for lymphocyte perforin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An inframe perforin gene deletion in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is associated with perforin expression.Am J Hematol. 2005 Jan;78(1):59-63. doi: 10.1002/ajh.20256. Am J Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15609274
-
Review of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in children with focus on Japanese experiences.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005 Mar;53(3):209-23. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2004.11.002. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15718147 Review.
-
A functional analysis of the putative polymorphisms A91V and N252S and 22 missense perforin mutations associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.Blood. 2005 Jun 15;105(12):4700-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4935. Epub 2005 Mar 8. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15755897
-
Perforin and lymphohistiocytic proliferative disorders.Br J Haematol. 2005 Mar;128(6):739-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05305.x. Br J Haematol. 2005. PMID: 15755277 Review.
-
Biology and treatment of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: importance of perforin in lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and triggering of apoptosis.Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002 May;38(5):305-9. doi: 10.1002/mpo.1340. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11979453 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of Lymphocyte Perforin as Focused Immunosuppressants for Infection and Autoimmunity.J Med Chem. 2022 Nov 10;65(21):14305-14325. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01338. Epub 2022 Oct 20. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36263926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human immunodeficiency syndromes affecting human natural killer cell cytolytic activity.Front Immunol. 2014 Jan 21;5:2. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00002. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24478771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic background of primary and familial HLH in Qatar: registry data and population study.Front Pediatr. 2024 May 9;12:1326489. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1326489. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38808104 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of perforin lysis: implications for protein disulfide isomerase proteins.Cell Immunol. 2009;255(1-2):82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2008.12.001. Epub 2009 Jan 14. Cell Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19147124 Free PMC article.
-
Graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) against mouse blast-crisis chronic myelogenous leukemia (BC-CML) and chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia (CP-CML): shared mechanisms of T cell killing, but programmed death ligands render CP-CML and not BC-CML GVL resistant.J Immunol. 2011 Aug 15;187(4):1653-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100311. Epub 2011 Jul 18. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21768400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trapani, J.A. 1998. Dual mechanisms of apoptosis induction by cytotoxic lymphocytes. Int. Rev. Cytol. 182:111–192. - PubMed
-
- Masson, D., and J. Tschopp. 1985. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 260:9069–9072. - PubMed
-
- Young, J.D., Z.A. Cohn, and E.R. Podack. 1986. The ninth component of complement and the pore-forming protein (perforin 1) from cytotoxic T cells: structural, immunological, and functional similarities. Science. 233:184–190. - PubMed
-
- Podack, E.R., and G. Dennert. 1983. Assembly of two types of tubules with putative cytolytic function by cloned natural killer cells. Nature. 302:442–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

