Sustained antiproliferative mechanisms by RB24, a targeted precursor of multiple inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor and a DNA alkylating agent in the A431 epidermal carcinoma of the vulva cell line
- PMID: 15365562
- PMCID: PMC2747684
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602098
Sustained antiproliferative mechanisms by RB24, a targeted precursor of multiple inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor and a DNA alkylating agent in the A431 epidermal carcinoma of the vulva cell line
Abstract
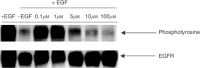
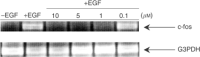
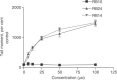
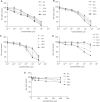
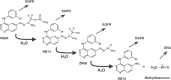
Recently, with the purpose of enhancing the potency of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-based therapies, we designed a novel strategy termed 'Cascade-release targeting' that seeks to develop molecules capable of degrading to multiple tyrosine kinase (TK) inhibitors and highly reactive electrophiles, in a stepwise fashion. Here we report on the first prototype of this model, RB24, a masked methyltriazene, that in addition to being an inhibitor on its own was designed to degrade to RB14, ZR08, RB10+a DNA alkylating methyldiazonium species. The cascade degradation of RB24 requires the generation of two reactive electrophiles: (a) an iminium ion and (b) a methyldiazonium ion. Thus, we surmise that these species could alkylate the active site of EGFR, thereby irreversibly blocking its action and that DNA damage could be induced by the methyldiazonium. Using the EGFR-overexpressing human epidermoid carcinoma of the vulva cell line, A431, we demonstrate herein that (a) RB24 and its derived species (e.g. RB14, ZR08) irreversibly inhibit EGFR autophosphorylation, (b) RB24 induced significant levels of DNA strand breaks, (c) sustained inhibition of EGFR by RB24 was associated with blockade of MAPK activation and c-fos gene expression, (d) RB24 induced irreversible cell growth inhibition with a 100-fold greater potency than Temodaltrade mark, a clinical methyltriazene. The pronounced growth inhibitory potency of RB24 was attributed to its ability to simultaneously damage DNA and irreversibly block EGFR TK activity.
Figures

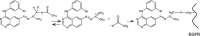
Similar articles
-
The combi-targeting concept: selective targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor- and Her2-expressing cancer cells by the complex combi-molecule RB24.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Jul;334(1):9-20. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.160085. Epub 2010 Mar 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20348204
-
The combi-targeting concept: mechanism of action of the pleiotropic combi-molecule RB24 and discovery of a novel cell signaling-based combination principle.Cell Signal. 2011 Apr;23(4):630-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.11.014. Epub 2010 Dec 5. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21138763
-
Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling by "Combi-triazene" BJ2000, a new probe for Combi-Targeting postulates.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Oct;303(1):238-46. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.039099. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. PMID: 12235257
-
Design of a chimeric 3-methyl-1,2,3-triazene with mixed receptor tyrosine kinase and DNA damaging properties: a novel tumor targeting strategy.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Mar;296(3):832-40. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11181914
-
Electrochemistry of chemotherapeutic alkylating agents and their interaction with DNA.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 Jan 5;222:115036. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.115036. Epub 2022 Sep 9. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023. PMID: 36244084 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Analysis of the Superior Efficacy of a Dual Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-DNA-Targeting Combi-Molecule in Comparison with Its Putative Prodrugs 6-Mono-Alkylamino- and 6,6-Dialkylaminoquinazoline in a Human Osteosarcoma Xenograft Model.Cells. 2023 Mar 16;12(6):914. doi: 10.3390/cells12060914. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980255 Free PMC article.
-
A type I combi-targeting approach for the design of molecules with enhanced potency against BRCA1/2 mutant- and O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (mgmt)- expressing tumour cells.BMC Cancer. 2017 Aug 11;17(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3504-1. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28800752 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor activation and inhibition in cellular response to chemotherapeutic combinational mimicries: the concept of divergent targeting.J Neurooncol. 2010 Dec;100(3):345-61. doi: 10.1007/s11060-010-0196-7. Epub 2010 May 14. J Neurooncol. 2010. PMID: 20467786
-
Quantitative Analysis of the Potency of Equimolar Two-Drug Combinations and Combi-Molecules Involving Kinase Inhibitors In Vitro: The Concept of Balanced Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 3;22(17):9569. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179569. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502481 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the dual targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor and the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase with a double arm hybrid molecule.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 12;9(80):35041-35055. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25120. eCollection 2018 Oct 12. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30416678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baig GU, Stevens MFG (1987) Antitumor imidazotetrazines. Part 12. Reactions of mitozolomide and its 3-alkyl congeners with oxygen, nitrogen, halogen, and carbon nucleophiles. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1: 665–667
-
- Banerjee R, Rachid Z, McNamee J, Jean-Claude BJ (2003) Synthesis of a prodrug designed to release multiple inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase and an alkylating agent: a novel tumour targeting concept. J Med Chem 46: 5546–5551 - PubMed
-
- Brahimi F, Matheson S, McNamee J, Tari A, Jean-Claude BJ (2002) Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling by ‘combi-triazene’ BJ2000, a new probe for the combi-targeting postulates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303: 238–246 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

