A discounting framework for choice with delayed and probabilistic rewards
- PMID: 15367080
- PMCID: PMC1382186
- DOI: 10.1037/0033-2909.130.5.769
A discounting framework for choice with delayed and probabilistic rewards
Abstract
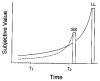
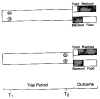
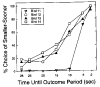
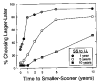
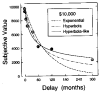
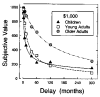
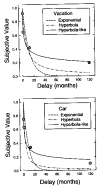
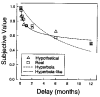
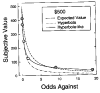
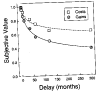
When choosing between delayed or uncertain outcomes, individuals discount the value of such outcomes on the basis of the expected time to or the likelihood of their occurrence. In an integrative review of the expanding experimental literature on discounting, the authors show that although the same form of hyperbola-like function describes discounting of both delayed and probabilistic outcomes, a variety of recent findings are inconsistent with a single-process account. The authors also review studies that compare discounting in different populations and discuss the theoretical and practical implications of the findings. The present effort illustrates the value of studying choice involving both delayed and probabilistic outcomes within a general discounting framework that uses similar experimental procedures and a common analytical approach.
((c) 2004 APA, all rights reserved)
Figures




Similar articles
-
Discounting of food, sex, and money.Psychon Bull Rev. 2014 Jun;21(3):794-802. doi: 10.3758/s13423-013-0557-2. Psychon Bull Rev. 2014. PMID: 24338570
-
The future is risky: discounting of delayed and uncertain outcomes.Behav Processes. 2013 Mar;94:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Behav Processes. 2013. PMID: 23201372
-
Discounting of delayed food rewards in pigeons and rats: is there a magnitude effect?J Exp Anal Behav. 2004 Jan;81(1):39-50. doi: 10.1901/jeab.2004.81-39. J Exp Anal Behav. 2004. PMID: 15113132 Free PMC article.
-
Delay discounting: Pigeon, rat, human--does it matter?J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2016 Apr;42(2):141-62. doi: 10.1037/xan0000097. Epub 2016 Feb 15. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2016. PMID: 26881899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bidding for delayed rewards: Accumulation as delay discounting, delay discounting as regulation, demand functions as corollary.J Exp Anal Behav. 2019 Sep;112(2):111-127. doi: 10.1002/jeab.545. J Exp Anal Behav. 2019. PMID: 31589338 Review.
Cited by
-
Theory Integration for Lifestyle Behavior Change in the Digital Age: An Adaptive Decision-Making Framework.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Apr 9;23(4):e17127. doi: 10.2196/17127. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33835036 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin, Central Dopamine D2 Receptors, and Monetary Reward Discounting in Obesity.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 20;10(7):e0133621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133621. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26192187 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a 5-HT4 receptor antagonist in the caudate nucleus on the performance of macaques in a delayed reward task.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 23;14(1):19619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70414-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39179718 Free PMC article.
-
Biphasic effects of alcohol on delay and probability discounting.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013 Jun;21(3):214-21. doi: 10.1037/a0032284. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23750692 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Influence of Musical and Monetary Rewards on Decision Making through Computational Modelling.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;14(2):124. doi: 10.3390/bs14020124. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ainslie G. Specious reward: A behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulse control. Psychological Bulletin. 1975;82:463–496. - PubMed
-
- Ainslie, G. (1992). Picoeconomics: The strategic interaction of successive motivational states within the person. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Ainslie, G. (2001). Breakdown of will. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Ainslie, G., & Haendel, V. (1983). The motives of the will. In E. Gottheil, K. A. Druley, T. E. Skoloda, & H. M. Waxman (Eds.), Etiologic aspects of alcohol and drug abuse (pp. 119–140). Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas.
-
- Ainslie G, Herrnstein RJ. Preference reversal and delayed reinforcement. Animal Learning & Behavior. 1981;9:476–482.

