5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside (AICAR) enhances GLUT2-dependent jejunal glucose transport: a possible role for AMPK
- PMID: 15367103
- PMCID: PMC1134720
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040694
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside (AICAR) enhances GLUT2-dependent jejunal glucose transport: a possible role for AMPK
Abstract
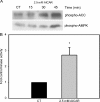
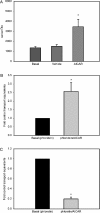
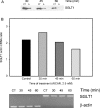
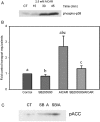
AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a key sensor of energy status within the cell. Activated by an increase in the AMP/ATP ratio, AMPK acts to limit cellular energy depletion by down-regulating selective ATP-dependent processes. The purpose of the present study was to determine the role of AMPK in regulating intestinal glucose transport. [3H]3-O-methyl glucose fluxes were measured in murine jejunum in the presence and absence of the AMPK activators AICAR (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside) and metformin and the p38 inhibitor, SB203580. To differentiate between a sodium-coupled (SGLT1) and diffusive (GLUT2) route of entry, fluxes were measured in the presence of the SGLT1 and GLUT2 inhibitors phloridzin and phloretin. Glucose transporter mRNA levels were measured by reverse transcriptase-PCR, and localization by Western blotting. Surface-expressed GLUT2 was assessed by luminal biotinylation. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase was analysed by Western blotting. We found that treatment of jejunal tissue with AICAR resulted in enhanced net glucose uptake and was associated with phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Inhibition of p38 abrogated the stimulation of AICAR-stimulated glucose uptake. Phloretin abolished the AICAR-mediated increase in glucose flux, whereas phloridzin had no effect, suggesting the involvement of GLUT2. In addition, AICAR decreased total protein levels of SGLT1, concurrently increasing levels of GLUT2 in the brush-border membrane. The anti-diabetic drug metformin, a known activator of AMPK, also induced the localization of GLUT2 to the luminal surface. We conclude that the activation of AMPK results in an up-regulation of non-energy requiring glucose uptake by GLUT2 and a concurrent down-regulation of sodium-dependent glucose transport.
Figures
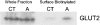

References
-
- Hardie D. G., Scott J. W., Pan D. A., Hudson E. R. Management of cellular energy by the AMP-activated protein kinase system. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Carling D., Clarke P. R., Zammit V. A., Hardie D. G. Purification and characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase. Copurification of acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase activities. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989;186:129–136. - PubMed
-
- Kemp B. E., Stapleton D., Campbell D. J., Chen Z. P., Murthy S., Walter M., Gupta A., Adams J. J., Katsis F., van Denderen B., et al. AMP-activated protein kinase, super metabolic regulator. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003;31:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Carling D. AMPK. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:R220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

