Routine sirolimus eluting stent implantation for unselected in-stent restenosis: insights from the rapamycin eluting stent evaluated at Rotterdam Cardiology Hospital (RESEARCH) registry
- PMID: 15367519
- PMCID: PMC1768512
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2003.025536
Routine sirolimus eluting stent implantation for unselected in-stent restenosis: insights from the rapamycin eluting stent evaluated at Rotterdam Cardiology Hospital (RESEARCH) registry
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of routine sirolimus eluting stent (SES) implantation for unselected patients with in-stent restenosis and to provide preliminary information about the angiographic outcome for lesion subgroups and for different in-stent restenosis patterns.
Design: Prospective, single centre registry.
Setting: Tertiary referral centre.
Patients: 44 consecutive patients (53 lesions) without previous brachytherapy who were treated with SES for in-stent restenosis were evaluated. Routine angiographic follow up was obtained at six months and the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events was evaluated.
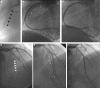
Results: At baseline, 42% of the lesions were focal, 21% diffuse, 26% proliferative, and 11% total occlusions. Small vessel size (reference diameter < or = 2.5 mm) was present in 49%, long lesions (> 20 mm) in 30%, treatment of bypass grafts in 13%, and bifurcation stenting in 18%. At follow up, post-SES restenosis was observed in 14.6%. No restenosis was observed in focal lesions. For more complex lesions, restenosis rates ranged from 20-25%. At the one year follow up, the incidence of death was 0, myocardial infarction 4.7% (n = 2), and target lesion revascularisation 16.3% (n = 7). The target lesion was revascularised because of restenosis in 11.6% (n = 5).
Conclusions: Routine SES implantation is highly effective for focal in-stent restenosis and appears to be a promising strategy for more complex patterns of restenosis.
Figures

References
-
- Lowe HC, Oesterle SN, Khachigian LM. Coronary in-stent restenosis: current status and future strategies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:183–93. - PubMed
-
- Mehran R , Dangas G, Abizaid AS, et al. Angiographic patterns of in-stent restenosis: classification and implications for long-term outcome. Circulation 1999;100:1872–8. - PubMed
-
- Leon MB, Teirstein PS, Moses JW, et al. Localized intracoronary gamma-radiation therapy to inhibit the recurrence of restenosis after stenting. N Engl J Med 2001;344:250–6. - PubMed
-
- Teirstein PS, Massullo V, Jani S, et al. Catheter-based radiotherapy to inhibit restenosis after coronary stenting. N Engl J Med 1997;336:1697–703. - PubMed
-
- Waksman R , White RL, Chan RC, et al. Intracoronary gamma-radiation therapy after angioplasty inhibits recurrence in patients with in-stent restenosis. Circulation 2000;101:2165–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
