Activation of TBK1 and IKKvarepsilon kinases by vesicular stomatitis virus infection and the role of viral ribonucleoprotein in the development of interferon antiviral immunity
- PMID: 15367631
- PMCID: PMC516426
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.19.10636-10649.2004
Activation of TBK1 and IKKvarepsilon kinases by vesicular stomatitis virus infection and the role of viral ribonucleoprotein in the development of interferon antiviral immunity
Abstract
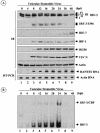
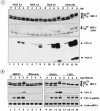
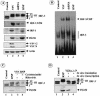
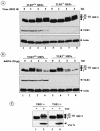
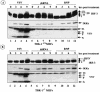
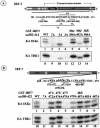
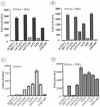
Mounting an immune response to a viral pathogen involves the initial recognition of viral antigens through Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent pathways and the subsequent triggering of signal transduction cascades. Among the many cellular kinases stimulated in response to virus infection, the noncanonical IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKKepsilon have been shown to phosphorylate and activate interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3) and IRF-7, leading to the production of alpha/beta interferons and the development of a cellular antiviral state. In the present study, we examine the activation of TBK1 and IKKepsilon kinases by vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infection in human lung epithelial A549 cells. We demonstrate that replication-competent VSV is required to induce activation of the IKK-related kinases and provide evidence that ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex of VSV generated intracellularly during virus replication can activate TBK1 and IKKepsilon activity. In TBK1-deficient cells, IRF-3 and IRF-7 activation is significantly reduced, although transcriptional upregulation of IKKepsilon following treatment with VSV, double-stranded RNA, or RNP partially compensates for the loss of TBK1. Biochemical analyses with purified TBK1 and IKKepsilon kinases in vitro demonstrate that the two kinases exhibit similar specificities with respect to IRF-3 and IRF-7 substrates and both kinases target serine residues that are important for full transcriptional activation of IRF-3 and IRF-7. These data suggest that intracellular RNP formation contributes to the early recognition of VSV infection, activates the catalytic activity of TBK1, and induces transcriptional upregulation of IKKepsilon in epithelial cells. Induction of IKKepsilon potentially functions as a component of the amplification mechanism involved in the establishment of the antiviral state.
Figures

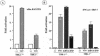
Similar articles
-
IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway.Nat Immunol. 2003 May;4(5):491-6. doi: 10.1038/ni921. Nat Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12692549
-
Inhibition of RIG-I-dependent signaling to the interferon pathway during hepatitis C virus expression and restoration of signaling by IKKepsilon.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):3969-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.3969-3978.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767399 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of TBK1 and IKKepsilon in lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of the interferon response in primary human macrophages.Eur J Immunol. 2007 Feb;37(2):528-39. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636090. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17236232
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections.Cell Res. 2005 Jun;15(6):407-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290309. Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15987599 Review.
Cited by
-
Interferon, Mx, and viral countermeasures.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007 Oct-Dec;18(5-6):425-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007. PMID: 17683972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitination of Immune System and Cancer Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1466:35-45. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-7288-9_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39546134 Review.
-
Toll-like receptor-independent triggering of dendritic cell maturation by viruses.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(7):3128-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.7.3128-3134.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16537581 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Interferon responses to norovirus infections: current and future perspectives.J Gen Virol. 2021 Oct;102(10):001660. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001660. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 34698626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel Toll-like receptor that recognizes vesicular stomatitis virus.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 11;286(6):4517-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.159590. Epub 2010 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21131352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexopoulou, L., A. C. Holt, R. Medzhitov, and R. A. Flavell. 2001. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732-738. - PubMed
-
- Au, W. C., P. A. Moore, W. Lowther, Y. T. Juang, and P. M. Pitha. 1995. Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferon-induced genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:11657-11661. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonnard, M., C. Mirtsos, S. Suzuki, K. Graham, J. Huang, M. Ng, A. Itie, A. Wakeham, A. Shahinian, W. J. Henzel, A. J. Elia, W. Shillinglaw, T. W. Mak, Z. Cao, and W. C. Yeh. 2000. Deficiency of T2K leads to apoptotic liver degeneration and impaired NF-κB-dependent gene transcription. EMBO J. 19:4976-4985. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu, W. M., D. Ostertag, Z. W. Li, L. Chang, Y. Chen, Y. Hu, B. Williams, J. Perrault, and M. Karin. 1999. JNK2 and IKKβ are required for activating the innate response to viral infection. Immunity 11:721-731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

