Selective decrease in paracellular conductance of tight junctions: role of the first extracellular domain of claudin-5
- PMID: 15367662
- PMCID: PMC516730
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8408-8417.2004
Selective decrease in paracellular conductance of tight junctions: role of the first extracellular domain of claudin-5
Abstract
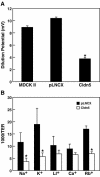
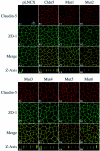
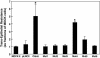
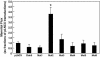
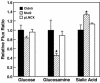
Claudin-5 is a protein component of many endothelial tight junctions, including those at the blood-brain barrier, a barrier that limits molecular exchanges between the central nervous system and the circulatory system. To test the contribution of claudin-5 to this barrier function of tight junctions, we expressed murine claudin-5 in Madin-Darby canine kidney II cells. The result was a fivefold increase in transepithelial resistance in claudin-5 transductants and a reduction in conductance of monovalent cations. However, the paracellular flux of neither neutral nor charged monosaccharides was significantly changed in claudin-5 transductants compared to controls. Therefore, expression of claudin-5 selectively decreased the permeability to ions. Additionally, site-directed mutations of particular amino acid residues in the first extracellular domain of claudin-5 altered the properties of the tight junctions formed in response to claudin-5 expression. In particular, the conserved cysteines were crucial: mutation of either cysteine abolishted the ability of claudin-5 to increase transepithelial resistance, and mutation of Cys(64) strikingly increased the paracellular flux of monosaccharides. These new insights into the functions of claudin-5 at the molecular level in tight junctions may account for some aspects of the blood-brain barrier's selective permeability.
Figures
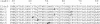


References
-
- Anderson, J. M. 2001. Molecular structure of tight junctions and their role in epithelial transport. News Physiol. Sci. 16:126-130. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, J. M., and C. M. Van Itallie. 1995. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am. J. Physiol. 269:G467-G475. - PubMed
-
- Antohe, F., L. Dobrila, C. Heltianu, N. Simionescu, and M. Simionescu. 1993. Albumin-binding proteins function in the receptor-mediated binding and transcytosis of albumin across cultured endothelial cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 60:268-275. - PubMed
-
- Balda, M. S., C. Flores-Maldonado, M. Cereijido, and K. Matter. 2000. Multiple domains of occludin are involved in the regulation of paracellular permeability. J. Cell Biochem. 78:85-96. - PubMed
-
- Balda, M. S., J. A. Whitney, C. Flores, S. Gonzalez, M. Cereijido, and K. Matter. 1996. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J. Cell Biol. 134:1031-1049. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
