Histone deacetylases 5 and 9 govern responsiveness of the heart to a subset of stress signals and play redundant roles in heart development
- PMID: 15367668
- PMCID: PMC516756
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8467-8476.2004
Histone deacetylases 5 and 9 govern responsiveness of the heart to a subset of stress signals and play redundant roles in heart development
Abstract
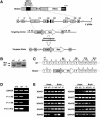
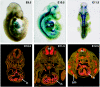
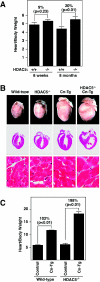
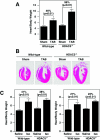
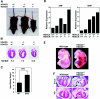
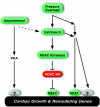
The adult heart responds to stress signals by hypertrophic growth, which is often accompanied by activation of a fetal cardiac gene program and eventual cardiac demise. We showed previously that histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9) acts as a suppressor of cardiac hypertrophy and that mice lacking HDAC9 are sensitized to cardiac stress signals. Here we report that mice lacking HDAC5 display a similar cardiac phenotype and develop profoundly enlarged hearts in response to pressure overload resulting from aortic constriction or constitutive cardiac activation of calcineurin, a transducer of cardiac stress signals. In contrast, mice lacking either HDAC5 or HDAC9 show a hypertrophic response to chronic beta-adrenergic stimulation identical to that of wild-type littermates, suggesting that these HDACs modulate a specific subset of cardiac stress response pathways. We also show that compound mutant mice lacking both HDAC5 and HDAC9 show a propensity for lethal ventricular septal defects and thin-walled myocardium. These findings reveal central roles for HDACs 5 and 9 in the suppression of a subset of cardiac stress signals as well as redundant functions in the control of cardiac development.
Figures
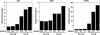
References
-
- Antos, C. L., T. A. McKinsey, M. Dreitz, L. M. Hollingsworth, C. L. Zhang, K. Schreiber, H. Rindt, R. J. Gorczynski, and E. N. Olson. 2003. Dose-dependent blockade to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 278:28930-28937. - PubMed
-
- Chien, K. R. 1999. Stress pathways and heart failure. Cell 98:555-558. - PubMed
-
- Davis, F. J., M. Gupta, B. Camoretti-Mercado, R. J. Schwartz, and M. P. Gupta. 2003. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activates serum response factor transcription activity by its dissociation from histone deacetylase, HDAC4. Implications in cardiac muscle gene regulation during hypertrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 278:20047-20058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
