Characterization of karyopherin cargoes reveals unique mechanisms of Kap121p-mediated nuclear import
- PMID: 15367670
- PMCID: PMC516728
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8487-8503.2004
Characterization of karyopherin cargoes reveals unique mechanisms of Kap121p-mediated nuclear import
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):10099
Abstract
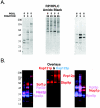
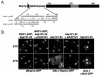
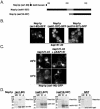
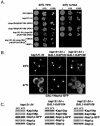
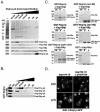
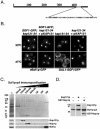
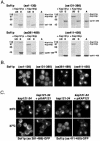
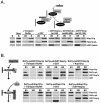
In yeast there are at least 14 members of the beta-karyopherin protein family that govern the movement of a diverse set of cargoes between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Knowledge of the cargoes carried by each karyopherin and insight into the mechanisms of transport are fundamental to understanding constitutive and regulated transport and elucidating how they impact normal cellular functions. Here, we have focused on the identification of nuclear import cargoes for the essential yeast beta-karyopherin, Kap121p. Using an overlay blot assay and coimmunopurification studies, we have identified 30 putative Kap121p cargoes. Among these were Nop1p and Sof1p, two essential trans-acting protein factors required at the early stages of ribosome biogenesis. Characterization of the Kap121p-Nop1p and Kap121p-Sof1p interactions demonstrated that, in addition to lysine-rich nuclear localization signals (NLSs), Kap121p recognizes a unique class of signals distinguished by the abundance of arginine and glycine residues and consequently termed rg-NLSs. Kap104p is also known to recognize rg-NLSs, and here we show that it compensates for the loss of Kap121p function. Sof1p is also transported by Kap121p; however, its import can be mediated by a piggyback mechanism with Nop1p bridging the interaction between Sof1p and Kap121p. Together, our data elucidate additional levels of complexity in these nuclear transport pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for cell-cycle-dependent nuclear import mediated by the karyopherin Kap121p.J Mol Biol. 2013 Jun 12;425(11):1852-1868. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.02.035. Epub 2013 Mar 28. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23541588
-
Identification and functional characterization of a novel nuclear localization signal present in the yeast Nab2 poly(A)+ RNA binding protein.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1449-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1449. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9488461 Free PMC article.
-
Karyopherins in nuclear pore biogenesis: a role for Kap121p in the assembly of Nup53p into nuclear pore complexes.J Cell Biol. 2002 Oct 28;159(2):267-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200203079. Epub 2002 Oct 28. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12403813 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct nuclear import and export pathways mediated by members of the karyopherin beta family.J Cell Biochem. 1998 Aug 1;70(2):231-9. J Cell Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9671229 Review.
-
Nuclear localization signals for four distinct karyopherin-β nuclear import systems.Biochem J. 2015 Jun 15;468(3):353-62. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150368. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26173234 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Rpb4p and Rpb7p subunits of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II by two pathways.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Dec;5(12):2092-103. doi: 10.1128/EC.00288-06. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 17056745 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple pathways regulate intracellular shuttling of MoKA, a co-activator of transcription factor KLF7.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(18):5060-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl659. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16990251 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic transport: a role for nonspecific competition in karyopherin-nucleoporin interactions.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 May;11(5):31-46. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.013656. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22357553 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear import of TFIIB is mediated by Kap114p, a karyopherin with multiple cargo-binding domains.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3200-10. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-11-0990. Epub 2005 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15888545 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the nuclear localization signals of 107 types of HPV L1 proteins by bioinformatic analysis.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2006 Feb;4(1):34-41. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(06)60014-4. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16689700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitchison, J. D., G. Blobel, and M. P. Rout. 1996. Kap104p: a karyopherin involved in the nuclear transport of messenger RNA binding proteins. Science 274:624-627. - PubMed
-
- Aitchison, J. D., M. P. Rout, M. Marelli, G. Blobel, and R. W. Wozniak. 1995. Two novel related yeast nucleoporins Nup170p and Nup157p: complementation with the vertebrate homologue Nup155p and functional interactions with the yeast nuclear pore-membrane protein Pom152p. J. Cell Biol. 131:1133-1148. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen, N. P., L. Huang, A. Burlingame, and M. Rexach. 2001. Proteomic analysis of nucleoporin interacting proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 276:29268-29274. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
