Loss of function but no gain of function caused by amino acid substitutions in the hexapeptide of Hoxa1 in vivo
- PMID: 15367676
- PMCID: PMC516739
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8567-8575.2004
Loss of function but no gain of function caused by amino acid substitutions in the hexapeptide of Hoxa1 in vivo
Abstract
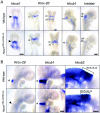
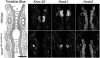
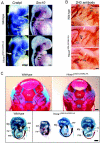
Homeodomain containing transcription factors of the Hox family play critical roles in patterning the anteroposterior embryonic body axis, as well as in controlling several steps of organogenesis. Several Hox proteins have been shown to cooperate with members of the Pbx family for the recognition and activation of identified target enhancers. Hox proteins contact Pbx via a conserved hexapeptide motif. Previous biochemical studies provided evidence that critical amino acid substitutions in the hexapeptide sequence of Hoxa1 abolish its interaction with Pbx. As a result, these substitutions also abolish Hoxa1 activity on known target enhancers in cellular models, suggesting that Hoxa1 activity relies on its capacity to interact with Pbx. Here, we show that mice with mutations in the Hoxa1 hexapeptide display hindbrain, cranial nerve, and skeletal defects highly reminiscent of those reported for the Hoxa1 loss of function. Since similar hexapeptide mutations in the mouse Hoxb8 and the Drosophila AbdA proteins result in activity modulation and gain of function, our data demonstrate that the functional importance of the hexapeptide in vivo differs according to the Hox proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Pbx interaction motif of Hoxa1 is essential for its oncogenic activity.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025247. Epub 2011 Sep 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21957483 Free PMC article.
-
Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 synergize in patterning the hindbrain, cranial nerves and second pharyngeal arch.Development. 1998 Mar;125(6):1123-36. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.6.1123. Development. 1998. PMID: 9463359
-
In vivo mutagenesis of the Hoxb8 hexapeptide domain leads to dominant homeotic transformations that mimic the loss-of-function mutations in genes of the Hoxb cluster.Dev Biol. 2003 Dec 1;264(1):77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.07.020. Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 14623233
-
Patterning the cranial neural crest: hindbrain segmentation and Hox gene plasticity.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000 Nov;1(2):116-24. doi: 10.1038/35039056. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11252774 Review.
-
Hox genes in neural patterning and circuit formation in the mouse hindbrain.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2009;88:139-67. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(09)88005-8. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19651304 Review.
Cited by
-
Selection of distinct Hox-Extradenticle interaction modes fine-tunes Hox protein activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 8;108(6):2276-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006964108. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21262810 Free PMC article.
-
Hindbrain induction and patterning during early vertebrate development.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Mar;76(5):941-960. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2974-x. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30519881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HOXA1 binds RBCK1/HOIL-1 and TRAF2 and modulates the TNF/NF-κB pathway in a transcription-independent manner.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7331-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw606. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27382069 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse fitness measures reveal incomplete functional redundancy of Hox paralogous group 1 proteins.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 5;12(4):e0174975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174975. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28380068 Free PMC article.
-
Generating spinal motor neuron diversity: a long quest for neuronal identity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Mar;71(5):813-29. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1398-x. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23765105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrow, J. R., and M. R. Capecchi. 1999. Compensatory defects associated with mutations in Hoxa1 restore normal palatogenesis to Hoxa2 mutants. Development 126:5011-5026. - PubMed
-
- Capecchi, M. R. 1997. Hox genes and mammalian development. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 62:273-281. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter, E. M., G. M. Goddard, O. Chisaka, N. R. Manley, and M. R. Capecchi. 1993. Loss of Hoxa-1 (Hox-1.6) function results in the reorganization of the murine hindbrain. Development 118:1063-1075. - PubMed
-
- Chan, S.-K., L. Jaffe, M. Capovilla, J. Botas, and R. Mann. 1994. The DNA binding specificity of Ultrabithorax is modulated by cooperative interactions with extradenticle, another homeoprotein. Cell 78:603-615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
