Epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent regulation of integrin-mediated signaling and cell cycle entry in epithelial cells
- PMID: 15367678
- PMCID: PMC516761
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8586-8599.2004
Epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent regulation of integrin-mediated signaling and cell cycle entry in epithelial cells
Abstract
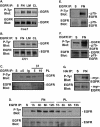
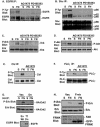
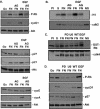
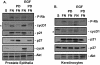
Integrin-mediated adhesion of epithelial cells to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins induces prolonged tyrosine phosphorylation and partial activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in an integrin-dependent and EGFR ligand-independent manner. Integrin-mediated activation of EGFR in epithelial cells is required for multiple signal transduction events previously shown to be induced by cell adhesion to matrix proteins, including tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc, Cbl, and phospholipase Cgamma, and activation of the Ras/Erk and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. In contrast, activation of focal adhesion kinase, Src, and protein kinase C, adhesion to matrix proteins, cell spreading, migration, and actin cytoskeletal rearrangements are induced independently of EGFR kinase activity. The ability of integrins to induce the activation of EGFR and its subsequent regulation of Erk and Akt activation permitted adhesion-dependent induction of cyclin D1 and p21, Rb phosphorylation, and activation of cdk4 in epithelial cells in the absence of exogenous growth factors. Adhesion of epithelial cells to the ECM failed to efficiently induce degradation of p27, to induce cdk2 activity, or to induce Myc and cyclin A synthesis; subsequently, cells did not progress into S phase. Treatment of ECM-adherent cells with EGF, or overexpression of EGFR or Myc, resulted in restoration of late-G(1) cell cycle events and progression into S phase. These results indicate that partial activation of EGFR by integrin receptors plays an important role in mediating events triggered by epithelial cell attachment to ECM; EGFR is necessary for activation of multiple integrin-induced signaling enzymes and sufficient for early events in G(1) cell cycle progression. Furthermore, these findings suggest that EGFR or Myc overexpression may provoke ligand-independent proliferation in matrix-attached cells in vivo and could contribute to carcinoma development.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Adhesion-regulated G1 cell cycle arrest in epithelial cells requires the downregulation of c-Myc.Oncogene. 2001 Jul 27;20(33):4554-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204609. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11494151
-
Resistance to small molecule inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor in malignant gliomas.Cancer Res. 2003 Nov 1;63(21):7443-50. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14612544
-
The proliferative effects of Pyropia yezoensis peptide on IEC-6 cells are mediated through the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Apr;35(4):909-14. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2111. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25716690 Free PMC article.
-
Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1833(12):3481-3498. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23830918 Review.
-
Crosstalk between Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (EGFR) and integrins in resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in solid tumors.Eur J Cell Biol. 2020 May;99(4):151083. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2020.151083. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32381360 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaceted roles of integrins in breast cancer metastasis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007 Sep;12(2-3):135-42. doi: 10.1007/s10911-007-9045-5. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007. PMID: 17602286 Review.
-
The glycan CA19-9 promotes pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in mice.Science. 2019 Jun 21;364(6446):1156-1162. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw3145. Science. 2019. PMID: 31221853 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of MLCK leads to disruption of cell-cell adhesion and invasive behavior of breast epithelial cells via increased expression of EGFR and ERK/JNK signaling.Oncogene. 2016 Aug 25;35(34):4495-508. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.508. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26876209
-
Substance P mediates antiapoptotic responses in human colonocytes by Akt activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 6;104(6):2013-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610664104. Epub 2007 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17264209 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins and cell-fate determination.J Cell Sci. 2009 Jan 15;122(Pt 2):171-7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.018945. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19118209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amati, B., K. Alevizopoulos, and J. Vlach. 1998. Myc and the cell cycle. Front. Biosci. 3:D250-D268. - PubMed
-
- Assoian, R. K., and M. A. Schwartz. 2001. Coordinate signaling by integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases in the regulation of G1 phase cell-cycle progression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11:48-53. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M. (ed.). 2000. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
