Phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus extracellular signal-regulated kinase/glycogen synthase kinase 3 site is required for the induction of adiponectin gene expression during the differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes
- PMID: 15367685
- PMCID: PMC516726
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8671-8680.2004
Phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus extracellular signal-regulated kinase/glycogen synthase kinase 3 site is required for the induction of adiponectin gene expression during the differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes
Abstract
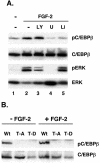
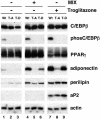
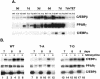
Stimulation of adipogenesis in mouse preadipocytes requires C/EBPbeta as well as activation of the MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway. In this study, we demonstrate that phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus ERK/glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) site regulates adiponectin gene expression during the C/EBPbeta-facilitated differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. First, we show that exposure of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to insulin, dexamethasone (DEX), and isobutylmethylxanthine (MIX) leads to the phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at threonine 188. Pretreating the cells with a MEK1-specific inhibitor (U0126) significantly attenuates this activity. Similarly, these effectors activate the phosphorylation of T188 within an ectopic C/EBPbeta overexpressed in Swiss mouse fibroblasts, and this event involves both MEK1 and GSK3 activity. We further show that expression of C/EBPbeta (p34kD LAP isoform) in Swiss mouse fibroblasts exposed to DEX, MIX, and insulin induces expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and some adiponectin but that it does not activate expression of FABP4/aP2. In fact, complete conversion of these fibroblasts into lipid-laden adipocytes, which includes activation of FABP4 and adiponectin expression, requires their exposure to a potent PPARgamma ligand such as troglitazone. Expression of a mutant C/EBPbeta in which threonine 188 has been modified to alanine (C/EBPbeta T188A) can induce PPARgamma production in the mouse fibroblasts, but it is incapable of stimulating adiponectin expression in the absence or presence of troglitazone. Interestingly, replacement of T188 with aspartic acid creates a C/EBPbeta molecule (C/EBPbeta T188D) that possesses adipogenic activity similar to that of the wild-type molecule. The absence of adiponectin expression correlates with a reduced amount of C/EBPalpha in the adipocytes expressing the T188A mutant suggesting that C/EBPalpha is required for expression of adiponectin. In fact, ectopic expression of PPARgamma in C/EBPalpha-deficient fibroblasts (NIH 3T3 cells) produces a modest amount of adiponectin, whereas expression of both PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha in NIH 3T3 cells facilitates production of abundant quantities of adiponectin. These data demonstrate that phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus ERK/GSK3 site is required for both C/EBPalpha and adiponectin gene expression during the differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A role for C/EBPbeta in regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 25;276(21):18464-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100797200. Epub 2001 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11279134
-
Sequential phosphorylation of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta by MAPK and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is required for adipogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jul 12;102(28):9766-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503891102. Epub 2005 Jun 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15985551 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of MEK/ERK signaling promotes adipogenesis by enhancing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma ) and C/EBPalpha gene expression during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 29;277(48):46226-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207776200. Epub 2002 Sep 20. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12270934
-
Regulation of PPARgamma activity during adipogenesis.Int J Obes (Lond). 2005 Mar;29 Suppl 1:S13-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802907. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005. PMID: 15711576 Review.
-
[Mechanical stretching inhibits adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells: the molecular mechanism and pharmacological regulation].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004 Nov;124(5):337-44. doi: 10.1254/fpj.124.337. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15502399 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Negative Regulation of Leptin-induced Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Formation by Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Activation in Hypothalamic Neurons.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 29;290(22):13669-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646885. Epub 2015 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25869131 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptide-producing dermal preadipocytes defend against Candida albicans skin infection via the FGFR-MEK-ERK pathway.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Nov 30;19(11):e1011754. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011754. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38032898 Free PMC article.
-
Adenomatous polyposis coli protein associates with C/EBP beta and increases Bacillus anthracis edema toxin-stimulated gene expression in macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19364-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.224543. Epub 2011 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21487015 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 8;6:38697. doi: 10.1038/srep38697. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27929048 Free PMC article.
-
Inside out: Bone marrow adipose tissue as a source of circulating adiponectin.Adipocyte. 2016 Mar 22;5(3):251-69. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2016.1149269. eCollection 2016 Jul-Sep. Adipocyte. 2016. PMID: 27617171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An, M. R., C. C. Hsieh, P. D. Reisner, J. P. Rabek, S. G. Scott, D. T. Kuninger, and J. Papaconstantinou. 1996. Evidence for posttranscriptional regulation of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ isoform expression during the lipopolysaccharide-mediated acute-phase response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2295-2306. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barak, Y., M. C. Nelson, E. S. Ong, Y. Z. Jones, P. Ruiz-Lozano, K. R. Chien, A. Koder, and R. M. Evans. 1999. PPARγ is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol. Cell 4:585-595. - PubMed
-
- Buck, M., V. Poli, T. Hunter, and M. Chojkier. 2001. C/EBPβ phosphorylation by RSK creates a functional XEXD caspase inhibitory box critical for cell survival. Mol. Cell 8:807-816. - PubMed
-
- Buck, M., V. Poli, P. van der Geer, M. Chojkier, and T. Hunter. 1999. Phosphorylation of rat serine 105 or mouse threonine 217 in C/EBP beta is required for hepatocyte proliferation induced by TGFα. Mol. Cell 4:1087-1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
