Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a regulates estrogen receptor alpha expression and is repressed by the Her-2/neu/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 15367686
- PMCID: PMC516736
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8681-8690.2004
Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a regulates estrogen receptor alpha expression and is repressed by the Her-2/neu/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway
Abstract
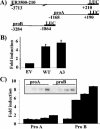
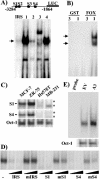
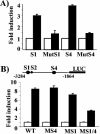
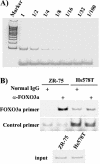
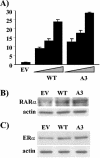
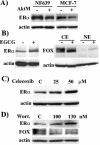
The expression status of the estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and that of the epidermal growth factor receptor Her-2/neu frequently correlate inversely in breast cancers. While ERalpha-dependent cancers respond to antiestrogen therapy, Her-2/neu-overexpressing cancers typically display resistance to antiestrogens and poor prognosis. In this report we have explored the mechanism linking the loss of expression of ERalpha in breast cancer cells with overexpression of Her-2/neu, which signals constitutively via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt kinase pathway. We identify for the first time the Forkhead box protein FOXO3a (formerly termed FKHRL-1), which is inactivated by Akt, as a key regulator of ERalpha gene transcription. In breast cancer cell lines, expression of ERalpha was correlated with active FOXO3a levels. Ectopic FOXO3a expression induced ERalpha protein levels and promoter activity, while a dominant negative FOXO3a decreased ERalpha levels. By using transient transfection, mobility shift assays, and site-directed mutagenesis, two major functional Forkhead binding sites were identified in the human ERalpha promoter B. A chromatin immunoprecipitation assay confirmed FOXO3a binding at these two sites. Ectopic FOXO3a induced estrogen response element-driven reporter activity and expression of ERalpha target genes. The constitutively activated myristylated Akt reduced ERalpha expression, whereas agents that negatively affect the PI3K/Akt pathway, i.e., wortmannin, celecoxib, and the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3 gallate, induced ERalpha. Thus, FOXO3a represents an important intracellular mediator of ERalpha expression, suggesting possible therapeutic intervention strategies for Her-2/neu-overexpressing refractory breast tumors.
Figures

References
-
- Brunet, A., A. Bonni, M. J. Zigmond, M. Z. Lin, P. Juo, L. S. Hu, M. J. Anderson, K. C. Arden, J. Blenis, and M. E. Greenberg. 1999. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857-868. - PubMed
-
- Brunet, A., G. Pages, and J. Pouyssegur. 1994. Constitutively active mutants of MAP kinase kinase (MEK1) induce growth factor-relaxation and oncogenicity when expressed in fibroblasts. Oncogene 9:3379-3387. - PubMed
-
- Burgess, A. W., H. S. Cho, C. Eigenbrot, K. M. Ferguson, T. P. Garrett, D. J. Leahy, M. A. Lemmon, M. X. Sliwkowski, C. W. Ward, and S. Yokoyama. 2003. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 12:541-552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
