DNA base pair resolution by single molecule force spectroscopy
- PMID: 15367697
- PMCID: PMC519116
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh826
DNA base pair resolution by single molecule force spectroscopy
Abstract
The forces that hold complementary strands of DNA together in a double helix, and the role of base mismatches in these, are examined by single molecule force spectroscopy using an atomic force microscope (AFM). These forces are important when considering the binding of proteins to DNA, since these proteins often mechanically stretch the DNA during their action. In AFM measurement of forces, there is an inherent instrumental limitation that makes it difficult to compare results from different experimental runs. This is circumvented by using an oligonucleotide microarray, which allowed a direct comparison of the forces between perfectly matched short oligonucleotides and those containing a single or double mismatch. Through this greatly increased sensitivity, the force contribution of a single AT base pair was derived. The results indicate that the contribution to forces from the stacking interactions is more important than that from hydrogen bonding.
Figures

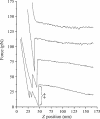
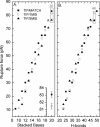
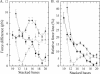
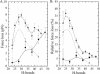


References
-
- Breslauer K.J. (1995) Extracting thermodynamic data from equilibrium melting curves for oligonucleotide order–disorder transitions. Methods Enzymol., 259, 221–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

