Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases
- PMID: 15367757
- PMCID: PMC2828947
- DOI: 10.1126/stke.2502004re13
Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases
Abstract
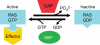
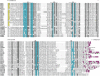
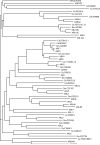
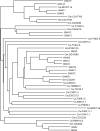
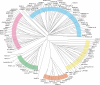
The tumor oncoproteins HRAS, KRAS, and NRAS are the founding members of a larger family of at least 35 related human proteins. Using a somewhat broader definition of sequence similarity reveals a more extended superfamily of more than 170 RAS-related proteins. The RAS superfamily of GTP (guanosine triphosphate) hydrolysis-coupled signal transduction relay proteins can be subclassified into RAS, RHO, RAB, and ARF families, as well as the closely related Galpha family. The members of each family can, in turn, be arranged into evolutionarily conserved branches. These groupings reflect structural, biochemical, and functional conservation. Recent findings have provided insights into the signaling characteristics of representative members of most RAS superfamily branches. The analysis presented here may serve as a guide for predicting the function of numerous uncharacterized superfamily members. Also described are guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) distinct from members of the RAS superfamily. These related proteins employ GTP binding and GTPase domains in diverse structural contexts, expanding the scope of their function in humans.
Figures








References
-
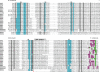
- Human Genome Nomenclature Committee All prediced proteins discussed in this review are supported by both genomic and cDNA sequences. (HGNC, http://www.gene.ucl.ac.uk/nomenclature) symbols are used throughout (Table 1 provides a list of some common gene names corresponding to HGNC symbols)
-
-
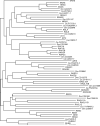
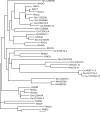
ClustalW was used for all sequence alignments and for the generation of dendrograms. Only GTPase domains were used in the analysis (i.e., extraneous sequences were removed).
-
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: Conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991;349:117–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
